Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
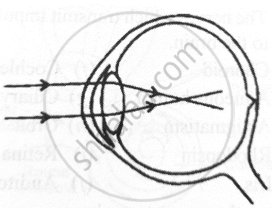
Write the function of the human eye and label parts of the figure given below.

उत्तर
- Double convex transparent crystalline lens: It provides small adjustments of the focal length to focus the image. This lens creates a real and inverted image of an object on the screen inside the eye.
- Optic nerve: The sensitive cells on the retina get excited when light falls on them and generate electric signals. The optic nerve carries these signals to the brain.
- Retina: It is the screen inside the human eye which contains light-sensitive cells. Image of an object is formed on this screen.
- Pupil: The pupil contracts or widens depending on the intensity of light incident on the eye.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
List the parts of the human eye that control the amount of light entering into it. Explain how they perform this function.
Distinguish between: aqueous humor and vitreous humor
A person got his eyes tested by an optician. The prescription for the spectacle lenses to be made reads :
Left eye : +2.50 D
Right eye : +2.00 D
Which lens bends the light rays more strongly?
Name two parts of the eye which refract light rays (or bend light rays).
Out of rods and cones m the retina of your eye:
which work in dim light?
What is the least distance of distinct vision for a normal human eye?
Give the scientific names of the following parts of the eye:
carries signals from an eye to the brain.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The part of eye which alters the size of the pupil is............
What change is made in the eye to enable it to focus on objects situated at different distances? Illustrate your answer with the help of diagrams.
How is the amount of light entering the eye controlled?
Which of the following changes occur when you walk out of bright sunshine into a poorly lit room?
(a) the pupil becomes larger
(b) the lens becomes thicker
(c) the ciliary muscle relaxes
(d) the pupil becomes smaller
Explain why, when it is getting dark at night, it is impossible to make out the colour of cars on the road.
After testing the eyes of a child, the optician has prescribed the following lenses for his spectacles:
Left eye : + 2.00 D
Right eye : + 2.25 D
The child is suffering from the defect of vision called:
(a) short-sightedness
(b) long-sightedness
(c) cataract
(d) presbyopia
Name two animals having eyes:
one the sides of the head.
The animals called predators have:
(a) both the eyes on the sides
(b) one eye on the side and one at the front
(c) one eye on the front and one at the back
(d) both the eyes at the front
What happens to the image distance in the normal human eye when we decrease the distance of an object, say 10 m to 1 m? Justify your answer.
Name the following:
Fluid present in the posterior chamber of the eye.
Mention, if the following statement is True or False
Rods are responsible for vision in the dark
State the Function:
Iris
Choose the Odd One Out:
For the normal human eye, the near point is at ___________ cm.
In a relaxed state, the focal length of healthy eyes is _______.
Write the name.
The fleshy screen behind cornea.
The image of the object in the human eye is formed on the cross screen.
The image of an object at an infinite distance is obtained in a real and erect form through a convex magnifying glass.
Why the human eye is compared with camera?
In a myopic eye, the image of the object is formed
The pigmented circular area seen in front of the eye:
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Answer the questions that follow:
- Give the scientific term for the defect.
- Mention one possible reason for the defect.
- What type of lens can be used to correct the defect?
Boojho while waving his hand very fast in front of his eyes, observes that his fingers appear blurred. What could be the reason for it?
Select the option with incorrect identification:
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e. Power of accommodation |
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e. Power of accommodation |
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
| 1 | Retina | a | Path way of light |
| 2 | Pupil | b | Far point comes closer |
| 3 | Ciliary muscles | c | near point moves away |
| 4 | Myopia | d | Screen of the eye |
| 5 | Hypermetropoia | e | Power of accomodation |
Given below is a cross section of the human eye. Match the structures marked (a) to (e) with their correct functions:
Example: (f) - 6. Holds the lens in position
| Cross section of Human Eye | Functions | |
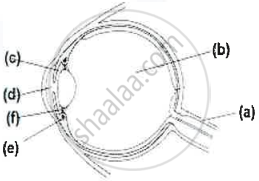 |
1. | Protects retina |
| 2. | Regulates the size of the pupil | |
| 3. | Alters the shape of the lens | |
| 4. | Keeps the lens moist | |
| 5. | Transmits nerve impulses to brain | |
| 6. | Holds the lens in position |
Chris was watching the display of fireworks in the sky.

- Trace the path of the light rays using the following terms:
Fovea, Lens, Conjunctiva, Pupil, Cornea. - Name the nerve that carries the impulse for vision to the brain.
State the functions of the following:
Iris
State the functions of the following:
Ciliary muscles
Name the following:
Capacity of the eye to focus at different distances.
With reference to human eye answer the question that follow:
Name the part of the eye associated with the regulation of the shape of lens.
