Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
_______ is a combination of two convex lenses with small focal length.
पर्याय
simple microscope
compound microscope
telescope
none of these
उत्तर
Compound microscope is a combination of two convex lenses with small focal length.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student focuses the image of a well-illuminated distant object on a screen using a convex lens. After that, he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image on the screen by adjusting the lens.
(i) In which direction, towards the screen or away from the screen, does he move the lens?
(ii) What happens to the size of the image? Does it decrease or increase?
(iii) What happens to the image on the screen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using a lens:-
(a) Which type of lens should be use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length 'F' of the lens should be place the candle flame so as to get (i) a magnified, and (ii) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagram to show the formation of the image in each case?
If you focus the image of a distant object, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image of this object on the screen would be:
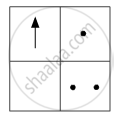
(a)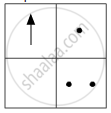
(b)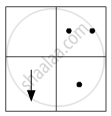
(c)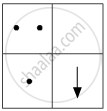
(d)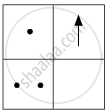
"A lens can form a magnified erect image as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." State the nature of this lens and draw ray diagrams to justify the above statement. Mark the positions of O, F and 2F in the diagram.
Write one condition where it does not bend when entering a medium of different optical density.
Where should an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size as the object is obtained using a convex lens?
A beam of light travelling in a rectangular glass slab emerges into air. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a refracted ray of light.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at 90° (that is, perpendicular to the glass block)
Where should an object be placed in order to use a convex lens as a magnifying glass?
With the help of a labelled diagram explain how a convex lens converges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the convex lens on the diagram.
Calculate the focal length of a convex lens which produces a virtual image at a distance of 50 cm of an object placed 20 cm in front of it.
If the object is moved to a point only 3 cm away from the lens, what is the new position, height and nature of the image?
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.15 m
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Rewrite the image distances in the correct order.
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What would be the image distance if the object distance was 90 cm?
What type of lens is used to correct
hypermetropia
In figure , name the ray which represents the correct path of light while emerging out through
a glass block.
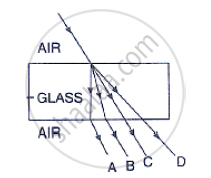
The diagrams (a) and (b) in Figure below show the refraction of a monochromatic ray of light through a parallel sided glass block and a prism respectively. In each diagram, label the incident, refracted emergent rays and the angle of deviation.

Study the diagram given below.
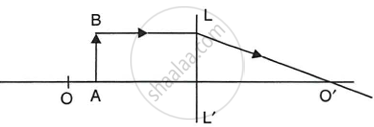
- Name the lens LL’.
- What are the points O and O’ called?
- Complete the diagram to form the image of the object AB.
- State the three characteristics of the image.
- Name a device in which this action of lens is used.
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Name the type of lens.
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is of the same size as the object?
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations:
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –60 | +12 |
| 2 | –30 | +15 |
| 3 | –20 | +20 |
| 4 | –15 | +30 |
| 5 | –12 | +60 |
| 6 | –9 | +90 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? State reason for your answer.
(b) For what object-distance (u) is the corresponding image-distance (v) not correct? How did you arrive at this conclusion?
(c) Choose an appropriate scale to draw a ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of magnification.
When you focus the image of a distant flag, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image as it appears on the screen is
(A)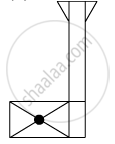
(B)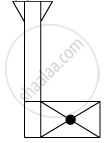
(C)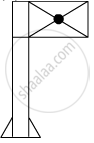
(D)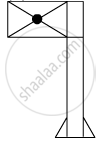
If you are to determine to focal length of a convex lens, you should have
(A) a convex lens and a screen
(B) a convex lens and a lens holder
(C) a lens holder, a screen holder and a scale
(D) a convex lens, a screen, holder for them and a scale
An object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find (i) the position (ii) the magnification and (iii) the nature of the image formed.
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
A pin 2 cm long is placed 12 cm away from a convex lens at right angles to the principal axis. If the focal length of the lens is 20 cm, by scale drawing find the size of the image and its magnification.
State two applications of a convex lens.
An object 4.0 cm in size, is placed 25.0 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15.0 cm.
(i) At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image?
(ii) Find the size of the image.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in this case.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of photographic camera.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.

- Where is the above type of lens construction used?
- What type of image is formed by an objective lens?
- What happens instead of placing at Fo if the object is placed in between O and Fo?
Differentiate convex lens and concave lens.

The above image shows a thin lens with a focal length of 5m.
- What is the kind of lens shown in the above figure?
- If a real inverted image is to be formed by this lens at a distance of 7m from the optical centre, then show with calculation where should the object be placed.
- Draw a neatly labelled diagram of the image formation mentioned in (ii).
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
