Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
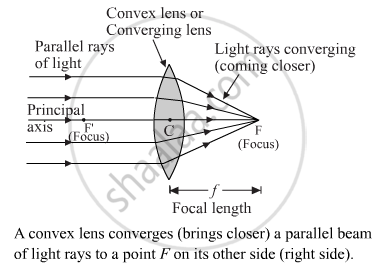
With the help of a labelled diagram explain how a convex lens converges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the convex lens on the diagram.
उत्तर
Suppose that a parallel beam of light rays falls on a convex lens as shown in the figure. These light rays are parallel to one another and also to the axis of the lens. The incident rays pass through the convex lens and get refracted according to the laws of refraction. All the rays, after passing through the convex lens, converge at the same point F, on the other side of the lens. The point F is called the principal focus of the convex lens. Thus, the point of convergence of the parallel beam of light rays to a single point is called the focus of the lens.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student focuses the image of a well-illuminated distant object on a screen using a convex lens. After that, he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image on the screen by adjusting the lens.
(i) In which direction, towards the screen or away from the screen, does he move the lens?
(ii) What happens to the size of the image? Does it decrease or increase?
(iii) What happens to the image on the screen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its virtual, erect and magnified image?
In order to obtain a real image twice the size of the object with a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, the object distance should be:
(a) more than 5 cm but less than 10 cm
(b) more than 10 cm but less than 15 cm
(c) more than 15 cm but less than 30 cm
(d) more than 30 cm but less than 60 cm
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Rewrite the image distances in the correct order.
Which causes more bending (or more refraction) of light rays passing through it : a convex lens of long focal length or a convex lens of short focal length?
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. State two more characteristics of the image.
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object. Name the lens.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as an erecting lens in terrestrial telescope.
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex lens.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
