Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
_______ times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
पर्याय
5
10
20
60
उत्तर
20 times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
If an object is placed at the focus of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its virtual, erect and magnified image?
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the formation of image of a finite object placed in front of convex lens between f and 2f. Give two characteristics of the image so formed.
List some things that convex lens and concave mirror have in common.
An object is placed f and 2f of a convex lens. Which of the following statements correctly describes its image?
(a) real, larger than the object
(b) erect, smaller than the object
(c) inverted, same size as object
(d) virtual, larger than the object
A convex lens of focal length 8 cm forms a real image of the same size as the object. The distance between object and its image will be:
(a) 8 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 32 cm
What is the position of image when an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm?
A convex lens produces an inverted image magnified three times of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from it. Calculate focal length of the lens.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.15 m
What kind of lens can form:
an inverted diminished image?
What kind of lens can form:
am erect diminished image?
A convex lens of focal length 10 cm is placed in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. The focal length of this combination of lenses will be:
(a) +10 cm
(b) +20 cm
(c) −10 cm
(d) −20 cm
Complete the following sentence.
A long-sighted person cannot see ........... objects clearly. Long-sightedness can be corrected by using .............. lenses.
A convex lens is placed in water. Its focal length will ______.
Study the diagram below.
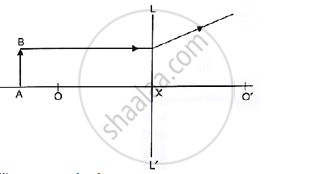
what are the points O, O’ called?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is at infinity?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is of the same size as the object?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is inverted and enlarged?
When you focus the image of a distant flag, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image as it appears on the screen is
(A)
(B)
(C)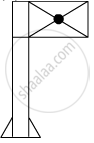
(D)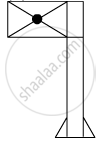
A teacher sets up the stand carrying a convex lens of focal length 15 cm at 42.7 cm mark on the optical bench. He asks four students A, B, C and D to suggest the position of screen on the optical bench so that a distinct image of a distant tree is obtained almost immediately on it. The positions suggested by the students were as
A. 12.7 cm
B. 29.7 cm
C. 57.7 cm
D. 72.7 cm
The correct position of the screen was suggested by
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
If you are to determine to focal length of a convex lens, you should have
(A) a convex lens and a screen
(B) a convex lens and a lens holder
(C) a lens holder, a screen holder and a scale
(D) a convex lens, a screen, holder for them and a scale
An object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find (i) the position (ii) the magnification and (iii) the nature of the image formed.
State two applications of a convex lens.
Write the three characteristics of the image formed by a convex lens of focal length 20 cm for the object at distance (i) 10 cm, (ii) 30 cm, (iii) 40 cm, (iv) 60 cm from the lens.
Can a normal convex lens behave like a concave lens and vice-versa?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to form an inverted and enlarged image? Will the image be real or virtual? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate your answer.

Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Convex lens is also known as ______.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
