Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
_______ times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
विकल्प
5
10
20
60
उत्तर
20 times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to study the image formation by it for the various positions of the object. He observes that when he places the object at 27 cm, the location of the image is at 54 cm on the other side of the lens. Identify from the following diagram the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used to draw the corresponding ray diagram.
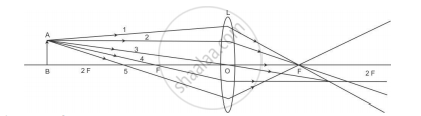
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 5
(C) 2, 4 and 5
(D) 2, 3 and 4
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
"A lens can form a magnified erect image as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." State the nature of this lens and draw ray diagrams to justify the above statement. Mark the positions of O, F and 2F in the diagram.
When a ray of light enters from one medium to another having different optical densities it bends. Why does this phenomenon occur?
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find :
1) the position of the image
2) nature of the image
A beam of light travelling in a rectangular glass slab emerges into air. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path.
f the image formed by a convex lens is of the same size as that of the object, what is the position of the image with respect to the lens?
For what position of an object a real, diminished image is formed by a convex lens?
Distinguish between a convex lens and concave lens. Which of the two is a converging lens : convex lens of concave lens?
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the formation of image of a finite object placed in front of convex lens between f and 2f. Give two characteristics of the image so formed.
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed at infinity (considerable distance) in front of a convex lens. State three characteristics of the image so formed.
You eye contains a convex lens. Why is it unwise to look at the sun?
An object is placed f and 2f of a convex lens. Which of the following statements correctly describes its image?
(a) real, larger than the object
(b) erect, smaller than the object
(c) inverted, same size as object
(d) virtual, larger than the object
A burning candle whose flame is 1.5 cm tall is placed at a certain distance in front of a convex lens. An image of candle flame is received on a white screen kept behind the lens. The image of flame also measures 1.5 cm. If f is the focal length of convex lens, the candle is placed:
(a) at f
(b) between f and 2f
(c) at 2f
(d) beyond 2f
Calculate the focal length of a convex lens which produces a virtual image at a distance of 50 cm of an object placed 20 cm in front of it.
A convex lens of focal length 15 cm produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed:
(a) at a distance of 15 cm
(b) between 15 cm and 30 cm
(c) at less than 15 cm
(d) beyond 30 cm
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Which of the object distances gives the biggest image?
What type of images can a convex lens make?
A beam of parallel light rays is incident through the holes on one side of a box and emerges out through the holes on its opposite side as shown in the diagram below:
Which of the following could be inside the box?
(a) a rectangular glass block
(b) a concave lens
(c) a convex lens
(d) a glass prism
The focal length of a thin convex lens is ______ than that of a thick convex lens.
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens. State three characteristics of the image.
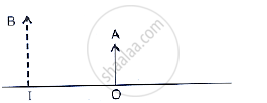
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object. Name the lens.
A student places a 8.0 cm tall object perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. He obtains a sharp image of the object on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. What will be the nature (inverted, erect, magnified, diminished) of the image he obtains on a screen? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
Point out the difference between a convex lens and a concave lens.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as an erecting lens in terrestrial telescope.
What happens to the image formed by a convex lens if its lower part is blackened?
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used in cine projector.
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a virtual and magnified image.
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a real image of the same size
In sunglasses, both of its surfaces are curved, yet their behaviour is neither like a convex lens nor like a concave lens. State the reason.
Diagram shows an object AB placed on the principal axis B of a convex lens placed in air. F1 and F2 are the two foci of the lens.
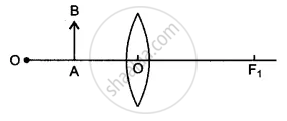
(i) Copy the diagram:
Draw a ray of light starting from B and passing through O. Show the same ray after refraction by the lens. Draw another ray from B which passes through F2 after refraction by the lens. Locate the final image
(ii) Is the image real or virtual?
_______ is a combination of two convex lenses with small focal length.
Write the name.
The lens used in simple microscope.
Differentiate convex lens and concave lens.
Which of the following statements is true?
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
