Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
पर्याय
Eye piece
Magnifier
Kaleidoscope
Telescope
उत्तर
Kaleidoscope
Explanation-
Kaleidoscope uses mirrors while other devices make use of lenses.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations :
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –100 | +25 |
| 2 | –60 | +30 |
| 3 | –40 | +40 |
| 4 | –30 | +60 |
| 5 | –25 | +100 |
| 6 | –15 | +120 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason to justify your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of the observation which is not correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion?
(c) Select an appropriate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S.No. 2. Also find the approximate value of magnification.
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
A ray of light travelling in water emerges into air. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path.
An object is placed at a distance equal to 2f in front of a convex lens. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image. State two characteristics of the image formed.
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the size, nature and position of the image formed by a convex lens when an object is placed beyond 2f in front of the lens.
A convex lens of focal length 8 cm forms a real image of the same size as the object. The distance between object and its image will be:
(a) 8 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 32 cm
What is the position of image when an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm?
A convex lens of focal length 6 cm is held 4 cm from a newspaper which has print 0.5 cm high. By calculation, determine the size and nature of the image produced.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.50 m
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What is the focal length of this lens?
Which type of lenses are:
thicker in the middle than at the edges?
How would a pencil look like if you saw it through How would a pencil look like if you saw it through
An object is placed 20 cm from (a) a converging lens, and (b) a diverging lens, of focal length 15 cm. Calculate the image position and magnification in each case.
Which causes more bending (or more refraction) of light rays passing through it : a convex lens of long focal length or a convex lens of short focal length?
The focal lengths of four convex lenses P, Q, R and S are 20 cm, 15 cm, 5 cm and 10 cm, respectively. The lens having greatest power is :
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
What kind of lens is used to correct
long-sightedness?
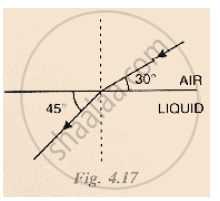
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from sir to a liquid.
(a) write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
(b) use snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a convex lens.
The focal length of a thin convex lens is ______ than that of a thick convex lens.
Study the diagram below.
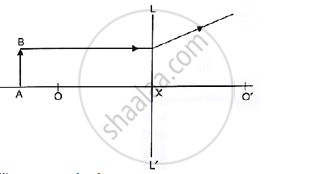
what are the points O, O’ called?
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object State whether the image is real or virtual
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is at infinity?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is inverted and enlarged?
A student places a 8.0 cm tall object perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. He obtains a sharp image of the object on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. What will be the nature (inverted, erect, magnified, diminished) of the image he obtains on a screen? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
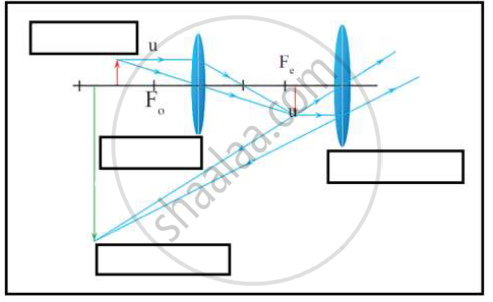
i. Which type of microscope has the arrangement of lenses shown in the adjoining figure?
ii. Label the figure correctly.
iii. Write the working of this microscope.
iv. Where does this microscope used?
v. Suggest a way to increase the efficiency of this microscope.
Answer the following question.
List four precautions which a student should observe while determining the focal length of a given convex lens by obtaining an image of a distant object on a screen.
Point out the difference between a convex lens and a concave lens.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of astronomical telescope.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of photographic camera.
What happens to the image formed by a convex lens if its lower part is blackened?
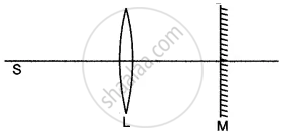
In the figure given below L is a convex lens, M is a plane mirror and S is a point source of light. Rays of light from the source S return to their point of origin. Complete the ray diagram to show this. What is the point S called?
An object is placed in front of a convex lens such that the image formed has the same size as that of the object. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this.
Define the terms principal foci and focal lengths as applied to a convex lens, and show them with the help of proper diagrams.
Can one bum a piece of paper in daylight by just using a convex lens instead of a match or any direct flame? Support your answer with the help of an appropriate ray diagram.
Simple microscope : Number of convex lens one : : compound microscope : _______
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
