Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
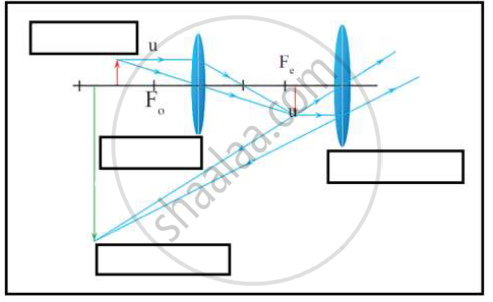
i. Which type of microscope has the arrangement of lenses shown in the adjoining figure?
ii. Label the figure correctly.
iii. Write the working of this microscope.
iv. Where does this microscope used?
v. Suggest a way to increase the efficiency of this microscope.
उत्तर
i. Compound microscope
ii. Scientifically and technically correct figure.
(Object, Objective lens, Eye piece, Image)
iii. Magnification is obtained by the combined effect of two
lenses. The magnification occurs in two stages. The image formed by the first lens acts as the object for the second lens. Clear image can be obtained by adjusting the distance between two lenses.
iv. To study small sized objects like blood cells, animal and plant
cells, bacteria.
v. Any relevant remedy (For example, Selection of lens with
appropriate focal length)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation
"A lens can form a magnified erect image as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." State the nature of this lens and draw ray diagrams to justify the above statement. Mark the positions of O, F and 2F in the diagram.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size as the object is obtained using a convex lens
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
A beam of light travelling in air is incident of water. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in water.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a refracted ray of light.
If an object is placed at the focus of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
Where should an object be placed in order to use a convex lens as a magnifying glass?
For what position of an object a real, diminished image is formed by a convex lens?
If an object is at a considerable distance (or infinity) in front of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
Explain with the help of a diagram, why the convex lens is also called a converging lens.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a real magnified image by a convex lens. (In your sketch the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus of lens should be shown clearly).
An object is placed at a distance equal to 2f in front of a convex lens. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image. State two characteristics of the image formed.
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the size, nature and position of the image formed by a convex lens when an object is placed beyond 2f in front of the lens.
Find the position and nature of the image of an object 5 cm high and 10 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 6 cm.
An object 50 cm tall is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens. Its 20 cm tall image is formed on the screen placed at a distance of 10 cm from the lens. Calculate the focal length of the lens.
What kind of lens can form:
an inverted magnified image?
An object is placed 20 cm from (a) a converging lens, and (b) a diverging lens, of focal length 15 cm. Calculate the image position and magnification in each case.
A camera fitted with a lens of focal length 50 mm is being used to photograph a flower that is 5 cm in diameter. The flower is placed 20 cm in front of the camera lens.
At what distance from the film should the lens be adjusted to obtain a sharp image of the flower?
The focal lengths of four convex lenses P, Q, R and S are 20 cm, 15 cm, 5 cm and 10 cm, respectively. The lens having greatest power is :
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
What type of lens is used to correct
hypermetropia
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a convex lens.
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. State two more characteristics of the image.
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object State whether the image is real or virtual
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is upright and enlarged?
A convex lens has a divergent action and a concave lens has a convergent action.
Draw neat diagram to show the
Convergent action of a convex lens,
(a) What type of a lens can be used as a magnifying glass?
(b) Show by a ray diagram the formation of a real image by simple magnifying lens.
An object 4.0 cm in size, is placed 25.0 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15.0 cm.
(i) At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image?
(ii) Find the size of the image.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in this case.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used in cine projector.
A concave mirror and convex lens are held in water. What changes, if any, do you expect in their focal length?
In sunglasses, both of its surfaces are curved, yet their behaviour is neither like a convex lens nor like a concave lens. State the reason.
Define the terms principal foci and focal lengths as applied to a convex lens, and show them with the help of proper diagrams.
_______ is a combination of two convex lenses with small focal length.
Write the name.
The lens used in simple microscope.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
