Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
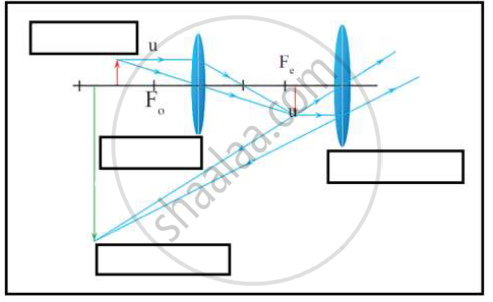
i. Which type of microscope has the arrangement of lenses shown in the adjoining figure?
ii. Label the figure correctly.
iii. Write the working of this microscope.
iv. Where does this microscope used?
v. Suggest a way to increase the efficiency of this microscope.
Solution
i. Compound microscope
ii. Scientifically and technically correct figure.
(Object, Objective lens, Eye piece, Image)
iii. Magnification is obtained by the combined effect of two
lenses. The magnification occurs in two stages. The image formed by the first lens acts as the object for the second lens. Clear image can be obtained by adjusting the distance between two lenses.
iv. To study small sized objects like blood cells, animal and plant
cells, bacteria.
v. Any relevant remedy (For example, Selection of lens with
appropriate focal length)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object of height 2.5 cm is placed at a distance of 15 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical 'O', principal focus F and height of the image on the diagram.
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

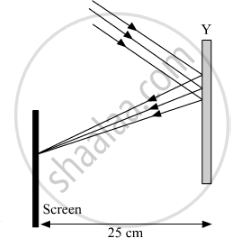
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find :
1) the position of the image
2) nature of the image
For what position of an object a real, diminished image is formed by a convex lens?
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the formation of image of a finite object placed in front of convex lens between f and 2f. Give two characteristics of the image so formed.
An object is placed at a distance equal to 2f in front of a convex lens. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image. State two characteristics of the image formed.
With the help of a labelled diagram explain how a convex lens converges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the convex lens on the diagram.
Name one simple optical instrument in which the above arrangement of convex lens is used.
A convex lens has a focal length of 10 cm. At which of the following position should an object be placed so that this convex lens may act as a magnifying glass?
(a) 15 cm
(b) 7 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 25 cm
In order to obtain a real image twice the size of the object with a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, the object distance should be:
(a) more than 5 cm but less than 10 cm
(b) more than 10 cm but less than 15 cm
(c) more than 15 cm but less than 30 cm
(d) more than 30 cm but less than 60 cm
An object 4 cm high is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
Calculate the focal length of a convex lens which produces a virtual image at a distance of 50 cm of an object placed 20 cm in front of it.
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Which of the object distances gives the biggest image?
A beam of parallel light rays is incident through the holes on one side of a box and emerges out through the holes on its opposite side as shown in the diagram below:
Which of the following could be inside the box?
(a) a rectangular glass block
(b) a concave lens
(c) a convex lens
(d) a glass prism
What kind of lens can form:
an inverted diminished image?
A camera fitted with a lens of focal length 50 mm is being used to photograph a flower that is 5 cm in diameter. The flower is placed 20 cm in front of the camera lens.
At what distance from the film should the lens be adjusted to obtain a sharp image of the flower?
What kind of lens is used to correct
long-sightedness?
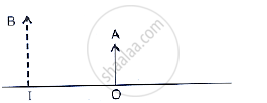
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens. State three characteristics of the image.
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object. Name the lens.
An object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find (i) the position (ii) the magnification and (iii) the nature of the image formed.
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
A convex lens forms an inverted image of size same as that of the object which is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of the lens. Find: The position of image
State two applications of a convex lens.
Point out the difference between a convex lens and a concave lens.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of photographic camera.
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a real image of the same size
We can burn a piece of paper by focussing the sun rays by using a particular type of lens. Name the type of lens used for the above purpose. Draw a ray diagram to support your answer.
How will you determine the focal length of a convex lens by the plane mirror method?
Diagram shows an object AB placed on the principal axis B of a convex lens placed in air. F1 and F2 are the two foci of the lens.
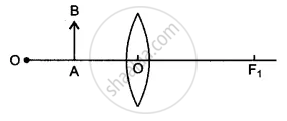
(i) Copy the diagram:
Draw a ray of light starting from B and passing through O. Show the same ray after refraction by the lens. Draw another ray from B which passes through F2 after refraction by the lens. Locate the final image
(ii) Is the image real or virtual?
_______ times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.

The above image shows a thin lens with a focal length of 5m.
- What is the kind of lens shown in the above figure?
- If a real inverted image is to be formed by this lens at a distance of 7m from the optical centre, then show with calculation where should the object be placed.
- Draw a neatly labelled diagram of the image formation mentioned in (ii).
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex lens.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
