Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
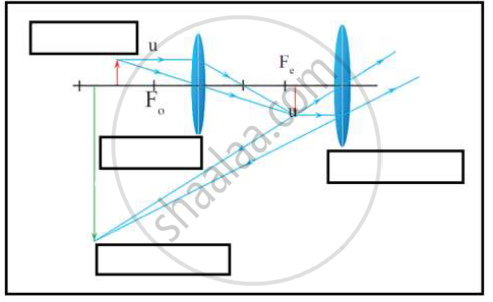
i. Which type of microscope has the arrangement of lenses shown in the adjoining figure?
ii. Label the figure correctly.
iii. Write the working of this microscope.
iv. Where does this microscope used?
v. Suggest a way to increase the efficiency of this microscope.
उत्तर
i. Compound microscope
ii. Scientifically and technically correct figure.
(Object, Objective lens, Eye piece, Image)
iii. Magnification is obtained by the combined effect of two
lenses. The magnification occurs in two stages. The image formed by the first lens acts as the object for the second lens. Clear image can be obtained by adjusting the distance between two lenses.
iv. To study small sized objects like blood cells, animal and plant
cells, bacteria.
v. Any relevant remedy (For example, Selection of lens with
appropriate focal length)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation
"A convex lens can form a magnified erect as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." Draw ray diagram to justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the lens in each case.
An object 5 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
A student places a candle flame at a distance of about 60 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm and focuses the image of the flame on a screen. After that he gradually moves the flame towards the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-toward or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the image?
(b) How does the size of the image change?
(c) How does the intensity of the image change as the flame moves towards the lens?
(d) Approximately for what distance between the flame and the lens, the image formed on the screen is inverted and of the same size?
Write one condition where it does not bend when entering a medium of different optical density.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from air into an optically denser medium.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from an optically denser medium into air.
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the formation of image of a finite object placed in front of convex lens between f and 2f. Give two characteristics of the image so formed.
An object is placed at a distance equal to 2f in front of a convex lens. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image. State two characteristics of the image formed.
State whether convex lens has a real focus or a virtual focus.
List some things that convex lens and concave mirror have in common.
Name one simple optical instrument in which the above arrangement of convex lens is used.
A convex lens of focal length 8 cm forms a real image of the same size as the object. The distance between object and its image will be:
(a) 8 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 32 cm
Find the position and nature of the image of an object 5 cm high and 10 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 6 cm.
Calculate the focal length of a convex lens which produces a virtual image at a distance of 50 cm of an object placed 20 cm in front of it.
Which of the above two cases illustrates the working of a magnifying glass?
What kind of lens can form:
an erect magnified image?
Complete the following sentence.
A long-sighted person cannot see ........... objects clearly. Long-sightedness can be corrected by using .............. lenses.
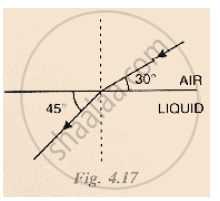
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from sir to a liquid.
(a) write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
(b) use snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Name the type of lens.
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. State two more characteristics of the image.
A lens forms an inverted image of an object. Name the kind of lens.
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object State whether the image is real or virtual
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is upright and enlarged?
A convex lens has a divergent action and a concave lens has a convergent action.
While determining the focal length of a convex lens, you try to focus the image of a distant object formed by the lens on the screen. The image formed on the screen, as compared to the object, should be
(A) erect and highly diminished
(B) erect and enlarged
(C) inverted and enlarged
(D) inverted and highly diminished
The image obtained while finding the focal length of convex lens is ....................
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of astronomical telescope.
Write the three characteristics of the image formed by a convex lens of focal length 20 cm for the object at distance (i) 10 cm, (ii) 30 cm, (iii) 40 cm, (iv) 60 cm from the lens.
Why do we say that the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of a convex lens can be regarded as a sort of ‘turning points’ as far as the nature of the image formed by it is concerned?
Draw a diagram to show the convergent action of a convex lens by treating it as a combination of glass block and two triangular glass prisms, with the aid of two parallel incident rays.
Object at 2F1 of a convex lens : Image at 2F2 : : Object at F1 : _______
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Write scientific reason.
Adults need bifocal lens spectacle.
 |
 |
The above images are that of a specialized slide projector. Slides are small transparencies mounted in sturdy frames ideally suited to magnification and projection since they have a very high resolution and a high image quality. There is a tray where the slides are to be put into a particular orientation so that the viewers can see the enlarged erect images of the transparent slides. This means that the slides will have to be inserted upside down in the projector tray.
To show her students the images of insects that she investigated in the lab, Mrs. Iyer brought a slide projector. Her slide projector produced 500 times enlarged and inverted image of a slide on a screen 10 m away.
a. Based on the text and data given in the above paragraph, what kind of lens must the slide projector have?
b. If v is the symbol used for image distance and u for object distance then with one reason state what will be the sign for `"𝑣"/"𝑢"` in the given case?
c. A slide projector has a convex lens with a focal length of 20 cm. The slide is placed upside down 21 cm from the lens. How far away should the screen be placed from the slide projector’s lens so that the slide is in focus?
OR
c. When a slide is placed 15 cm behind the lens in the projector, an image is formed 3 m in front of the lens. If the focal length of the lens is 14 cm, draw a ray diagram to show image formation. (not to scale)
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
