Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Diagram shows an object AB placed on the principal axis B of a convex lens placed in air. F1 and F2 are the two foci of the lens.
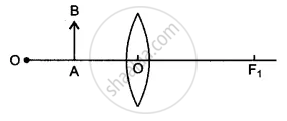
(i) Copy the diagram:
Draw a ray of light starting from B and passing through O. Show the same ray after refraction by the lens. Draw another ray from B which passes through F2 after refraction by the lens. Locate the final image
(ii) Is the image real or virtual?
Solution
(i)
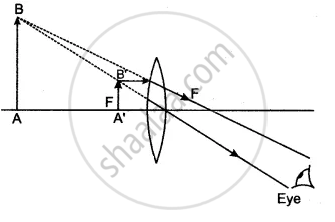
(ii) Image is virtual.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
In a certain murder investigation, it was important to discover whether the victim was long-sighted or short-sighted. How could a detective decide by examining his spectacles?
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. State two more characteristics of the image.
A convex lens has a divergent action and a concave lens has a convergent action.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to form an inverted and enlarged image? Will the image be real or virtual? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate your answer.

A candle is placed between f and 2f a convex lens. Draw a ray diagram showing the position of the image.
_______ is a combination of two convex lenses with small focal length.

The above image shows a thin lens with a focal length of 5m.
- What is the kind of lens shown in the above figure?
- If a real inverted image is to be formed by this lens at a distance of 7m from the optical centre, then show with calculation where should the object be placed.
- Draw a neatly labelled diagram of the image formation mentioned in (ii).
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
