Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A convex lens forms an inverted image of size same as that of the object which is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of the lens. Find: The position of image
Solution
A convex lens forms an inverted, real, and an image of the same size as the object when the object is placed at 2f, i.e. (u = 2f).
In such cases, the image is formed at the point which is double the focal length on the other side of the lens (2f2).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Parallel rays of light are refracted by a convex lens to a point called the ........
An object is placed f and 2f of a convex lens. Which of the following statements correctly describes its image?
(a) real, larger than the object
(b) erect, smaller than the object
(c) inverted, same size as object
(d) virtual, larger than the object
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What is the focal length of this lens?
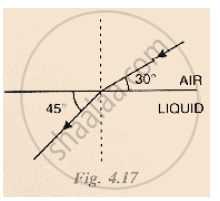
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from sir to a liquid.
(a) write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
(b) use snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.
Define the term principal axis of a lens.
Out of the five incident rays shown in the figure find the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used for locating the position of image formed by a convex lens: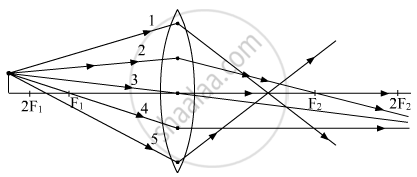
(A) 1, 2 and 3
(B) 2, 3 and 4
(C) 3, 4 and 5
(D) 1, 2 and 4
Draw neat diagram to show the
Convergent action of a convex lens,
What is the difference between a double convex and a bi-convex lens?
For a specific glass lens f = 0.5 m. This is the only information given to the student. Which type of lens is given to him and what is its power?
