Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For a normal human eye the near point is at _______.
पर्याय
2.1 cm
2.5 cm
25 cm
5 cm
उत्तर
For a normal human eye the near point is at 25 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the function of the following part of the human eye: ciliary muscles
Differentiate between: Rods and cones
The region of the vertebrate eye, where the optic nerve passes out of the retina, is called the
(a) fovea
(b) iris
(c) blind spot
(d) optic chaisma
With the help of ciliary muscles the human eye can change its curvature and thus alter the focal length of its lens. State the changes that occur in the curvature and focal length of the eye lens while viewing (a) a distance object, (b) nearby objects.
Name two parts of the eye which refract light rays (or bend light rays).
What is the name of:
the curved, transparent front surface of the eye?
How does the eye adjust to take account of an increase in brightness?
Give the scientific names of the following parts of the eye:
carries signals from an eye to the brain.
Give the scientific names of the following parts of the eye:
a hole in the middle of the iris.
What change is made in the eye to enable it to focus on objects situated at different distances? Illustrate your answer with the help of diagrams.
There are two types of light-sensitive cells in the human eye:
What is each type called?
What are rods and cones in the retina of an eye? Why is our night vision relatively poor compared to the night vision of an owl?
What happens to the size of pupil of our eye (i) in dim light (ii) in bright light?
Describe the working of the human eye with the help of the above diagram.
What shape are your eye-lenses:
when you look at your hand?
Among animals, the predators (like lions) have their eyes facing forward at the front of their heads, whereas the animals of prey (like rabbit) usually have eyes at the sides of their head. Why is this so?
Five persons A, B, C, D and E have diabetes, leukaemia, asthma, meningitis and hepatitis, respectively.
Which of these persons can donate eyes?
The region in the eyes where the rods and cones are located is the
Define the following:
Blind spot
Define the following:
Power of accommodation
Give the main function of the following:
Three semicircular canals
Choose the correct answer.
Rods are receptor of ______________
Name the following:
The focal length of the lens is altered by the contraction of which type of muscles.
Name the following:
The region in the eye where the rods and cones are located.
Name the following:
The type of lens used for correcting myopia.
Give Technical Term:
Name the part of the retina on which an object is focused for the clearest vision.
Give Technical Term:
The adjustment of the eye in order to obtain a clear vision of objects at different distances
State the Location:
Iris
State the Function:
Aqueous humour
State the Function:
Choroid coat in the eye
Long answer question
Draw the neat labelled diagram of the Sectional view of the human eye.
Vision defect that increases distance between the lens of the eye and retina of the eye is termed as myopia.
Write the function of the human eye and label parts of the figure given below.

Why the human eye is compared with camera?
A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in Figure . In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?
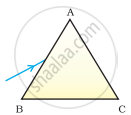 |
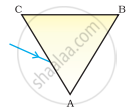 |
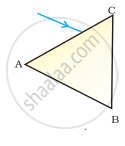 |
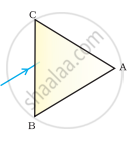 |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
We cannot distinguish colours in dim light. Explain giving suitable reasons.
Which part of the eye gets affected if someone is suffering from cataract? How is it treated?
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Pathway of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | f. Power of accommodation |
State the functions of the following:
Iris
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e. Power of accommodation |
