Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
For a normal human eye the near point is at _______.
Options
2.1 cm
2.5 cm
25 cm
5 cm
Solution
For a normal human eye the near point is at 25 cm.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Compare the following: Choroid and retina
Distinguish between: blind spot and yellow spot
The size of the pupil becomes ______ when you see in dim light.
Night birds have ______ cones than rods in their eyes.
Explain the mechanism of vision.
Name the part of the eye:
which controls the amount of light entering the eye.
What is the name of:
the curved, transparent front surface of the eye?
Give the scientific names of the following parts of the eye:
muscles which change the shape of the eye-lens.
There are two types of light-sensitive cells in the human eye:
What is each type called?
What happens to the size of pupil of our eye (i) in dim light (ii) in bright light?
Draw a simple diagram of the human eye and label clearly the cornea, iris, pupil, ciliary muscles, eye-lens, retina, optic nerve and blind spot.
What shape are your eye-lenses:
when you look at your hand?
What is presbyopia? Write two causes of this defect. Name the type of lens which can be used to correct presbyopia.
With both eyes open, a person's field of view is about:
(a) 90°
(b) 150°
(c) 180°
(d) 360°
With reference to the functioning of the eye, answer the question that follow:
Name the two structure in the eye responsible for bringing about the change in the shape of the lens.
State the function of each of the following parts of the human eye:
(i) Cornea
(ii) Iris
(iii) Pupil
(iv) Retina
Millions of people of the developing countries are suffering from corneal blindness. This disease can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of a donated eye. Your school has organised a campaign in the school and its neighbourhood in order to create awareness about this fact and motivate people to donate their eyes after death. How can you along with your classmates contribute in this noble cause? State the objectives of organising such campaigns in schools.
Name the following:
Short sightedness.
Give the main function of the following:
Three semicircular canals
Choose the correct answer.
Rods are receptor of ______________
What are the functions of tears?
What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye?
Differentiate between:
Vitreous humour and Aqueous humour.
Name the following:
The focal length of the lens is altered by the contraction of which type of muscles.
Name the following:
Fluid present in the posterior chamber of the eye.
State the Function:
Aqueous humour
A small hole of changing diameter at the centre of Iris is called _______.
Write the function of the human eye and label parts of the figure given below.

The muscular diaphragm that controls the size of the pupil is ____________.
The innermost layer of human eye is ______.
In human eye the part which allows light to enter into the eye is ______.
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e. Power of accommodation |
State the functions of the following:
Ciliary muscles
Name the following:
Place of no vision in the retina of the eye.
Name the following:
Kind of retinal cells sensitive to dim light.
Where is the following located?
Yellow spot
The figure given below refers to the vertical section of the eye of a mammal. Study the figure carefully and answer the following questions.
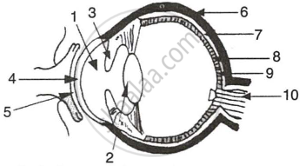 |
- Label the guidelines shown as 1 to 10.
- Write one important role of parts shown as 3 and 7.
- Write one structural difference between the parts shown as 9 and 10.
- Mention one functional difference between the parts shown as 6 and 8.
