Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What are the functions of tears?
Solution
The functions of tears:
(i) To lubricate the surface of the eye.
(ii) To wash away dust particles.
(iii) To help in killing germs.
(iv) To communicate emotions.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the function of retina in human eye.
Night birds have ______ cones than rods in their eyes.
The optical prescription for a pair of spectacles is :
Right eye : −3.50 D
Left eye : −4.00 D
Which lens has a greater focal length?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The part of eye which alters the size of the pupil is............
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The iris controls the amount of................entering the eye.
The eyes of a person are focused (i) on a nearby object, and (ii) on a distant object, turn by turn. In which case:
the focal length of eye-lens will be the maximum?
What happens to the eye when you enter a darkened cinema hall from bright sunshine? Give reason for your answer.
How does this affect the amount of light entering the eye?
Describe the working of the human eye with the help of the above diagram.
Mention if the following statement is true (T) or false (F) Give reason.
Ciliary muscles regulate the size of the pupil
What is a lacrimal gland?
Give the main function of the following:
Lachrymal glands
Choose the correct answer :
The rods and cones of a vertebrate retina function is to _________
Give Technical Term:
Name the part of the retina on which an object is focused for the clearest vision.
The image formed on the retina of the human eye is ____________.
The transparent membrane that keeps the eye moist is ______.
In human eye the part which allows light to enter into the eye is ______.
Given below is a cross section of the human eye. Match the structures marked (a) to (e) with their correct functions:
Example: (f) - 6. Holds the lens in position
| Cross section of Human Eye | Functions | |
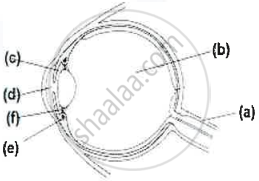 |
1. | Protects retina |
| 2. | Regulates the size of the pupil | |
| 3. | Alters the shape of the lens | |
| 4. | Keeps the lens moist | |
| 5. | Transmits nerve impulses to brain | |
| 6. | Holds the lens in position |
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e. Power of accommodation |
