Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Give the main function of the following:
Lachrymal glands
Solution
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
There are two types of light-sensitive cells in the human eye:
Where are they found?
Draw a simple diagram of the human eye and label clearly the cornea, iris, pupil, ciliary muscles, eye-lens, retina, optic nerve and blind spot.
The human eye possesses the power of accommodation. This is the power to:
(a) alter the diameter of the pupil as the intensity of light changes
(b) distinguish between lights of different colours
(c) focus on objects at different distances
(d) decide which of the two objects is closer.
Explain clearly why, a person who has lost the sight of one eye is at a disadvantage compared with the normal person who has two good eyes.
The animal which does not have eyes that look sideways is:
(a) Horse
(b) Chicken
(c) Lion
(d) Fish
Having two eyes gives a person:
(a) deeper field of view
(b) coloured field of view
(c) rear field of view
(d) wider field of view
The animals called predators have:
(a) both the eyes on the sides
(b) one eye on the side and one at the front
(c) one eye on the front and one at the back
(d) both the eyes at the front
The region in the eyes where the rods and cones are located is the
Mention if the following statement is true (T) or false (F) Give reason.
Sometimes medicines dropped into the eyes come into the nose and even throat
Mention if the following statement is true (T) or false (F) Give reason.
yellow spot of the retina is the region of colour vision
Give scientific reason:
One can sense colours only in bright light.
Choose the correct answer.
Rods are receptor of ______________
Name the following:
Yellow spot and ciliary muscles are found in.
Name the following:
Fluid present in the posterior chamber of the eye.
Give Technical Term:
The cells of the retina that are sensitive to colour.
Mention, if the following statement is True or False
Rods are responsible for vision in the dark
Complete the following sentence with appropriate Word
The part of the human eye where rod cells and cone cells are located is the:
Complete the paragraph by choosing the right options given below.
(minimum, near point, 25 cm, farthest, farthest distance, far point)
The _______ distance of an object from a normal eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye, is called the minimum distance of distinct vision. The position of the object at this distance is called the _______ of the eye, for a normal human eye, the near point is at _______. The _______ distance of an object from a human eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye is called _______ of distinct vision. The position of the object at this distance is called the _______ of the eye.
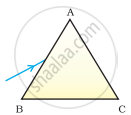
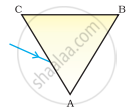
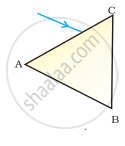
A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in Figure . In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?
 |
 |
 |
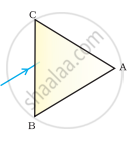 |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
Name the following:
Place of no vision in the retina of the eye.
