Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For a healthy human eye, the distant point is infinite distance.
पर्याय
Right
Wrong
उत्तर
For a healthy human eye, the distant point is infinite distance- Right
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw labelled diagrams of the following: Eye
Write short notes on the following: Retina
Distinguish between: blind spot and yellow spot
Explain the mechanism of vision.
Where is the image formed in a human eye?
Where does the greatest degree of refraction of light occur in the eye?
Fill in the following blank with suitable words:
When light is dim, the pupil becomes................
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
To bring light from a distant object to a focus on the retina of the eye, the convex eye-lens needs to be made..........
The eyes of a person are focused (i) on a nearby object, and (ii) on a distant object, turn by turn. In which case:
the focal length of eye-lens will be the maximum?
What happens to the size of pupil of our eye (i) in dim light (ii) in bright light?
Draw a simple diagram of the human eye and label clearly the cornea, iris, pupil, ciliary muscles, eye-lens, retina, optic nerve and blind spot.
How does the eye adjust itself to deal with light of varying intensity?
To focus the image of a nearby object on the retina of an eye:
(a) the distance between eye-lens and retina is increased
(b) the distance between eye-lens and retina is decreased
(c) the thickness of eye-lens is decreased
(d) the thickness of eye-lens is increased
Which of the following controls the amount of light entering the eye?
(a) ciliary muscles
(b) lens
(c) iris
(d) cornea
The human eye possesses the power of accommodation. This is the power to:
(a) alter the diameter of the pupil as the intensity of light changes
(b) distinguish between lights of different colours
(c) focus on objects at different distances
(d) decide which of the two objects is closer.
How does the eye change in order to focus on near or distant objects?
(a) The lens moves in or out
(b) The retina moves in or out
(c) The lens becomes thicker or thinner
(d) The pupil gets larger or smaller
Out of animals of prey and predators, which have their eyes:
on the opposite sides of their head?
State whether the following statement is true or false:
Rabbit has eyes which look sideways.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Having two eyes gives a ................field of view.
Name two animals having eyes:
one the sides of the head.
Having two eyes gives a person:
(a) deeper field of view
(b) coloured field of view
(c) rear field of view
(d) wider field of view
Mention if the following statement is true (T) or false (F) Give reason.
Short-sightedness and hyperopia are one and the same thing
Mention if the following statement is true (T) or false (F) Give reason.
Blind spot is called so because no image is formed on it.
Sometimes you remember a vivid picture of a dream you saw. What is the role of your eyes in this experience?
Give scientific reason:
We cannot clearly see an object kept at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye.
State the main functions of the following:
Coronary Artery
Explain the Term: Accommodation in the eye
Give Technical Term:
The adjustment of the eye in order to obtain a clear vision of objects at different distances
Mention, if the following statement is True or False
The least distance of distinct vision for the human eye is 25 cm
Complete the following sentence with appropriate Word
The part of the human eye where rod cells and cone cells are located is the:
Write the function of the human eye and label parts of the figure given below.

Assertion: Blind spot is a small area of the retina which is insensitive to light where the optic nerve leaves the eye.
Reason: There are no rods or cones present at the junction of the optic nerve and retina in the eye.
A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in Figure . In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?
 |
 |
 |
 |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
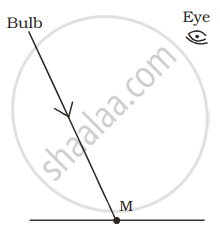
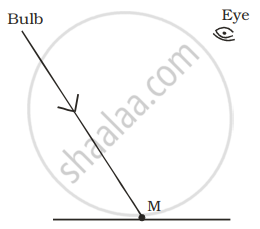
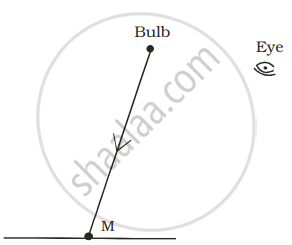
A tiny mirror M is fixed on a piece of cardboard placed on a table. The cardboard is illuminated by light from a bulb. The position of eye with respect to position of bulb is shown in the figure as A, B, C and D. In which position mirror will be visible?
 |
 |
 |
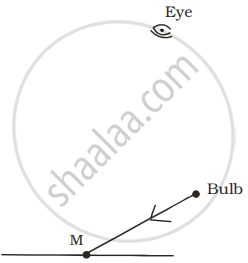 |
| (A) | (B) | (C) | (D) |
What kind of lens is there in our eyes? Where does it form the image of an object?
What is ‘white of the eye’?
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e. Power of accommodation |
Given below is a cross section of the human eye. Match the structures marked (a) to (e) with their correct functions:
Example: (f) - 6. Holds the lens in position
| Cross section of Human Eye | Functions | |
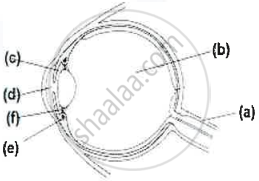 |
1. | Protects retina |
| 2. | Regulates the size of the pupil | |
| 3. | Alters the shape of the lens | |
| 4. | Keeps the lens moist | |
| 5. | Transmits nerve impulses to brain | |
| 6. | Holds the lens in position |
