Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A student focussed the image of a distant object using a device ‘X’ on a white screen ‘S’ as shown in the figure. If the distance of the screen from the device is 40 cm, select the correct statement about the device.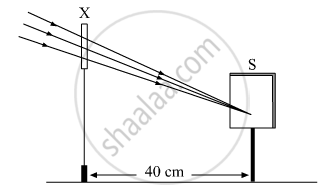
(A) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(B) The device X is a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm.
(C) The device X is a convex mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm.
(D) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 40 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
"A convex lens can form a magnified erect as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." Draw ray diagram to justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the lens in each case.
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find :
1) the position of the image
2) nature of the image
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the size, nature and position of the image formed by a convex lens when an object is placed beyond 2f in front of the lens.
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What would be the image distance if the object distance was 90 cm?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is inverted and enlarged?
State two applications of a convex lens.
Yesh find out F1 and F2 of symmetric convex lens experimentally then which conclusion is true.
A concave mirror and convex lens are held in water. What changes, if any, do you expect in their focal length?
Draw a ray diagram to illustrate the determination of the focal length of a convex lens using an auxiliary plane mirror.
