English Medium
Academic Year: 2010-2011
Date: March 2011
Advertisements
What are the various steps of food chain called?
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
What is the function of ozone in the upper atmosphere?
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
Write the electron dot structure of ethane molecule, C2H6.
Chapter:
What makes the earth’s atmosphere a heterogeneous mixture?
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
List any four characteristics of a good fuel.
Chapter: [0.14] Sources of Energy
What are non-renewable resources of energy? Give two examples of such resources.
Chapter: [0.14] Sources of Energy
How do you calculate the possible valency of an element from the electronic configuration of its atoms?
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
Calculate the valency of element X whose atomic number is 9.
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
On the basis of electronic configuration, how will you identify the first and the last element of a period?
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
State the two laws of reflection of light.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
The stars appear higher from horizon than they actually are. Explain why it is so.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Explain why the planets do not twinkle but the stars twinkle.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Write two differences between binary fission and multiple fission in a tabular form.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Explain the following:- Speciation
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Explain the following:- Natural Selection
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny?
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Advertisements
Out of HCl and CH3COOH, which one is a weak acid and why? Describe an activity to support your answer.
Chapter: [0.02] Acids, Bases and Salts
Two elements X and Y belong to group 1 and 2 respectively in the same period of periodic table. Compare them with respect to:
(i) the number of valence electrons in their atoms
(ii) their valencies
(iii) metallic character
(iv) the sizes of their atoms
(v) the formulae of their oxides
(vi) the formulae of their chlorides
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
Draw the ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this statement?
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Name a liquid whose mass density is less than that of water but it is optically denser than water.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
What eye defect is hypermetropia? Describe with a ray diagram how this defect of vision can be corrected by using an appropriate lens.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Write two examples of sexually transmitted diseases caused by virus.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Write two examples of sexually transmitted diseases caused by bacteri.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Explain how the transmission of virus and bacteria diseases be prevented?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Explain Mendel’s law of independent inheritance. Give one example.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
If the image formed by a lens is diminished in size and erect, for all positions of the object, what type of lens is it?
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Name the point on the lens through which a ray of light passes undeviated.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
An object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find (i) the position (ii) the magnification and (iii) the nature of the image formed.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
An object 5 cm high is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm.
(i) Draw the ray diagram and
(ii) Calculate the position and size of the image formed.
(iii) What is the nature of the image?
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Draw a diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower and label on it sepal, petal, ovary and stigma.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Write the names of male and female reproductive parts of a flower.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
What is fragmentation in organisms?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Name a multicellular organism which reproduces by fragmentation method.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
What is regeneration in organism?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Describe regeneration in Planaria with the help of a suitable diagram.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
In a tabular form, differentiate between ethanol and ethanoic acid under the following heads:
(i) Physical state
(ii) Taste
(iii) NaHCO3 test
(iv) Ester test
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Write a chemical reaction to show the dehydration of ethanol.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Advertisements
What is a soap?
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Why are soaps not suitable for washing clothes when the water is hard?
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Explain the action of soap in removing an oily spot from a piece of cloth.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student was given two permanent slides, one of binary fission in Amoeba and other of budding in yeast. He was asked to identify any one difference in the nucleus of the two. One such difference, he identified correctly was
(1) Presence of one nucleus in Amoeba, two in yeast cell and one in bud.
(2) Presence of two nuclei in centrally constricted Amoeba, one in yeast cell and one in its bud.
(3) Presence of two distant nuclei in Amoeba, one in yeast cell and two in bud.
(4) Presence of a single nucleus each in Amoeba, yeast cell and its attached bud.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Binary fission is observed in which one of the following figures?
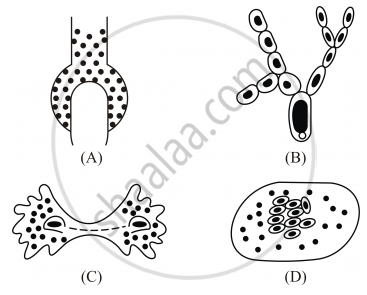
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
To determine the percentage of water absorbed by raisins, raisins are soaked in water for:
30 seconds
10 minutes
2 to 3 hours
24 hours
Chapter: [0.01] Chemical Reactions and Equations
Raisins are wiped off gently before final weighing with the help of
a filter paper
a cotton piece
a cloth piece
a polythene piece
Chapter: [0.01] Chemical Reactions and Equations
The step(s) necessary for determining the percentage of water absorbed by raisins is/are:
Raisins should be completely immersed in water
Raisins should be soaked in water for sufficient time
Gently wipe dry the soaked raisins
All of the above steps.
Chapter: [0.01] Chemical Reactions and Equations
Rahim recorded the following sets of observations while tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence.
|
S. No. |
Angle of incidence |
Angle of refraction |
Angle of emergence |
|
I |
45° |
41° |
45° |
|
II |
40° |
38° |
38° |
|
III |
45° |
41° |
40° |
|
IV |
41° |
45° |
41° |
The correct observation is recorded at serial number:
(1) I
(2) II
(3) III
(4) IV
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Four students A, B, C and D traced the paths of incident ray and the emergent ray by fixing pins P and Q for incident ray and pins R and S for emergent ray for a ray of light passing through a glass slab.
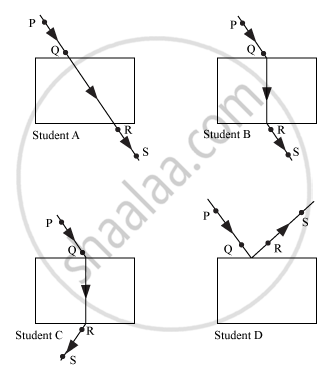
The correct emergent ray was traced by the student:
(1) A
(2) B
(3) C
(4) D
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Mohan obtained a sharp inverted image of a distant tree on the screen placed behind the lens. He then moved the screen and tried to look through the lens in the direction of the object. He would see:
(1) a blurred image on the wall of the laboratory.
(2) an erect image of the tree on the lens.
(3) no image as the screen has been removed
(4) an inverted image of the tree at the focus of the lens.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
For finding the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant object, one should use as the object.
(1) a well lit distant tree
(2) window grill in the class room
(3) any distant tree
(4) a lighted candle kept at the other end of the table.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
To find the focal length of a concave mirror Rahul focuses a distant object with this mirror. The chosen object should be
(1) a tree
(2) a building
(3) a window
(4) the sun
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
The colour of an aqueous solution of zinc sulphate as observed in the laboratory is:
(1) Green
(2) Yellow
(3) Blue
(4) Colourless
Chapter: [0.01] Chemical Reactions and Equations
To show that zinc is a more active metal than copper, the correct procedure is to:
(1) add dilute nitric acid on strips of both the metals.
(2) observe transmission of heat through strips of zinc and copper.
(3) prepare solution of zinc sulphate and hang strip of copper into it.
(4) prepare solution of copper sulphate and hang strip of zinc into it.
Chapter: [0.01] Chemical Reactions and Equations
Acetic acid smells like:
(1) a banana
(2) vinegar
(3) an orange
(4) a lemon
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Acetic acid solution turns:
(1) blue litmus red
(2) red litmus blue
(3) blue litmus colourless
(4) red litmus colourless
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
On adding NaHCO3 to acetic acid, a gas is evolved which turns lime water milky due to the formation of:
(1) Calcium bicarbonate
(2) Calcium hydroxide
(3) Calcium carbonate
(4) Calcium acetate
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A yeast cell in which budding occurs was seen to have:
(1) one bud cell
(2) two bud cell
(3) three bud cell
(4) a chain of bud cells
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 10 Science with solutions 2010 - 2011
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 10 Science-2011 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Science, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 10.
How CBSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Science will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
