Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will such a lens produce an image of the complete object? Support your answer with a ray diagram.
उत्तर
The convex lens will form complete image of an object, even if its one half is covered with black paper. It can be understood by the following two cases:
Case I
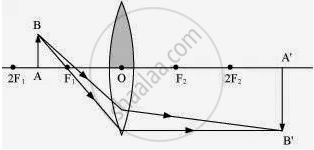
When the upper half of the lens is covered
In this case, a ray of light coming from the object will be refracted by the lower half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object, as shown in the above figure.
Case II
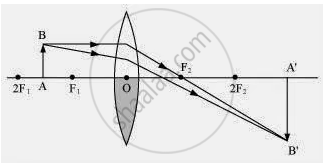
When the lower half of the lens is covered
In this case, a ray of light coming from the object is refracted by the upper half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object, as shown in the above figure.
संबंधित प्रश्न
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus.
(b) In the above ray diagram, mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case.
(c) Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre.
A student places a candle flame at a distance of about 60 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm and focuses the image of the flame on a screen. After that he gradually moves the flame towards the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-toward or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the image?
(b) How does the size of the image change?
(c) How does the intensity of the image change as the flame moves towards the lens?
(d) Approximately for what distance between the flame and the lens, the image formed on the screen is inverted and of the same size?
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

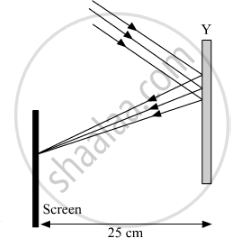
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
"A lens can form a magnified erect image as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." State the nature of this lens and draw ray diagrams to justify the above statement. Mark the positions of O, F and 2F in the diagram.
Complete the following table:
| Instrument | Number of Convex Lenses |
Use |
| Simple Microscope | .............. | .............. |
| Compound Microscope | .............. | .............. |
| Telescope | .............. | .............. |
If an object is at a considerable distance (or infinity) in front of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Parallel rays of light are refracted by a convex lens to a point called the ........
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The image in a convex lens depends upon the distance of the ........... from the lens.
A convex lens has a focal length of 10 cm. At which of the following position should an object be placed so that this convex lens may act as a magnifying glass?
(a) 15 cm
(b) 7 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 25 cm
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What would be the image distance if the object distance was 90 cm?
Which causes more bending (or more refraction) of light rays passing through it : a convex lens of long focal length or a convex lens of short focal length?
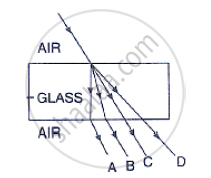
In figure , name the ray which represents the correct path of light while emerging out through
a glass block.
The diagrams (a) and (b) in Figure below show the refraction of a monochromatic ray of light through a parallel sided glass block and a prism respectively. In each diagram, label the incident, refracted emergent rays and the angle of deviation.

Show by a diagram the refraction of two light rays incident parallel to the principal axis on a convex lens by treating it as a combination of a glass slab and two triangular glass prisms.
State two applications of a convex lens.
Observe the following figure and answer the questions.
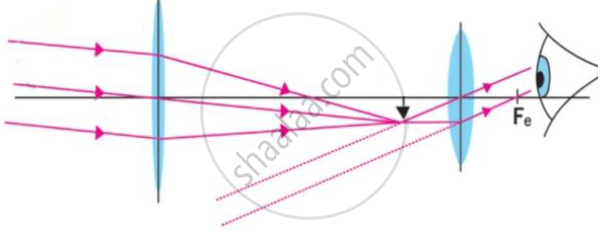
a) Which optical instrument shows arrangement of lenses as shown in the figure?
b) Write in brief the working of this optical instrument.
c) How can we get different magnifications in this optical instrument?
d) Draw the figure again and labelled it properly
Draw a ray diagram to illustrate the determination of the focal length of a convex lens using an auxiliary plane mirror.
We can burn a piece of paper by focussing the sun rays by using a particular type of lens. Name the type of lens used for the above purpose. Draw a ray diagram to support your answer.
Which of the following statements is true?
