Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will such a lens produce an image of the complete object? Support your answer with a ray diagram.
उत्तर
The convex lens will form complete image of an object, even if its one half is covered with black paper. It can be understood by the following two cases:
Case I
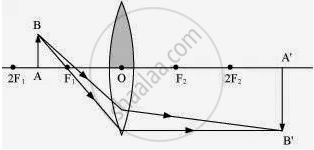
When the upper half of the lens is covered
In this case, a ray of light coming from the object will be refracted by the lower half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object, as shown in the above figure.
Case II
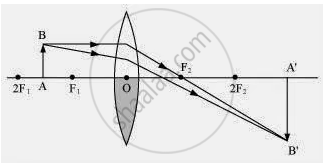
When the lower half of the lens is covered
In this case, a ray of light coming from the object is refracted by the upper half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object, as shown in the above figure.
संबंधित प्रश्न
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave lens when an object is placed in front of it.
(b) In the above diagram mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the concave lens in the case.
(c) Find the nature and power of a lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 at a distance of 40 cm from the optical centre.
A student has obtained a magnified image of a flame on a screen using a convex lens. To draw the corresponding ray diagram to show the image formation, which of the following two rays whose paths after refraction are shown, should he select ?
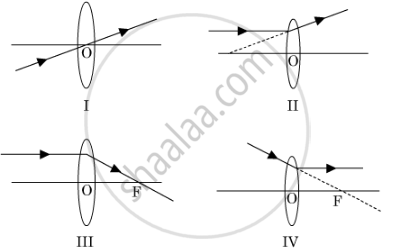
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) III and IV
(D) I and III
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size as the object is obtained using a convex lens
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at an angle other than 90° (that is, obliquely to the glass block).
State any two uses of convex lenses.
Calculate the focal length of a convex lens which produces a virtual image at a distance of 50 cm of an object placed 20 cm in front of it.
Which type of lenses are:
thicker in the middle than at the edges?
What type of images can a convex lens make?
What kind of lens can form:
an erect magnified image?
What would be the diameter of the image of the flower on the film?
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a convex lens.
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. State two more characteristics of the image.
Observe the following figure and answer the questions.
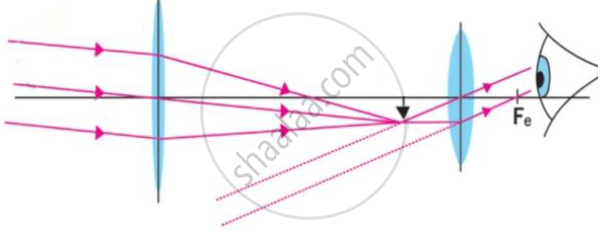
a) Which optical instrument shows arrangement of lenses as shown in the figure?
b) Write in brief the working of this optical instrument.
c) How can we get different magnifications in this optical instrument?
d) Draw the figure again and labelled it properly
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of photographic camera.
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a virtual and magnified image.
For a specific glass lens f = 0.5 m. This is the only information given to the student. Which type of lens is given to him and what is its power?
