Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
"A lens can form a magnified erect image as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." State the nature of this lens and draw ray diagrams to justify the above statement. Mark the positions of O, F and 2F in the diagram.
Solution
The lens is a convex in nature. Thus, it is a convex lens.
When the object is placed between the focus F1 and optical centre O a magnified erect image is formed as shown below.
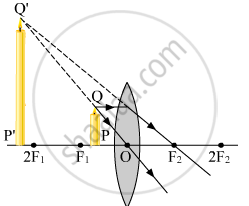
When the object is placed between the focus F1 and 2F1 a magnified inverted image is formed as shown below.
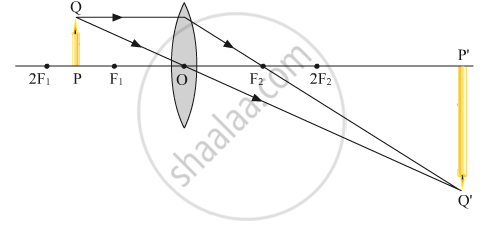
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations :
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –100 | +25 |
| 2 | –60 | +30 |
| 3 | –40 | +40 |
| 4 | –30 | +60 |
| 5 | –25 | +100 |
| 6 | –15 | +120 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason to justify your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of the observation which is not correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion?
(c) Select an appropriate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S.No. 2. Also find the approximate value of magnification.
The diagram given alongside shows a ray of light entering a rectangular block of glass.
(a) Copy the diagram and draw the normal at the point of entry.
(b) Draw the approximate path of the ray of light through the glass block and out of the other side.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.15 m
An object is placed 20 cm from (a) a converging lens, and (b) a diverging lens, of focal length 15 cm. Calculate the image position and magnification in each case.
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. Draw a diagram to illustrate it.
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is upright and enlarged?
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as an erecting lens in terrestrial telescope.
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a real image of the same size
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to form an inverted and enlarged image? Will the image be real or virtual? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate your answer.

