English Medium
Academic Year: 2016-2017
Date & Time: 21st March 2017, 12:30 pm
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
Write the molecular formula of the 2nd and 3rd member of the homologous series where the first member is ethyne.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Give the importance of variation in survival of species.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
In the following food chain, 20,000 J of energy was available to the plants. How much energy would be available to man in this chain?
Plants → Sheep → Man
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
You being an environmentalist are interested in contributing towards the conservation of natural resources. List four activities that you can do on your own.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
Why are coal and petroleum categorised as natural resources? Give a reason as to why they should be used judiciously.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
Distinguish between esterfication and saponification reaction with the help of the chemical equations for each.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
State one use of esterfication process.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
State one use of saponification process.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Give the structural formula of ethanol.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Write the name and structural formula of the compound obtained when ethanol is heated at 443 K with excess of conc. H2SO4. Also write chemical equation for the reaction stating the role of conc. H2SO4 in it.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
What is periodicity in properties of elements with reference to the Modern Periodic Table?
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
Why do all the elements of the same group have similar properties?
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
How does the tendency of elements to gain electrons change as we move from left to right in a period? State the reason of this change.
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
Write the electronic configuration of two elements X and Y whose atomic numbers are 20 and 17 respectively. Write the molecular formula of the compound formed when element X reacts with element Y. Draw the electron-dot structure of the product and also state the nature of the bond formed between both the elements.
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
How did Mendel explain that it is possible that a trait is inherited but not expressed in an organism?
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Organic Evolution cannot be equated with progress. Explain with the help of a suitable example.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Advertisements
List the two types of reproduction. Which one of the two is responsible for bringing in more variations in its progeny and how?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
What is vegetative propagation?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
List two advantages of vegetative propagation.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
State two disadvantages of vegetative propagation?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
List any four methods of contraception used by humans. State in brief two advantages of adopting such preventive methods.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
"A lens can form a magnified erect image as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." State the nature of this lens and draw ray diagrams to justify the above statement. Mark the positions of O, F and 2F in the diagram.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Define the term dispersion of white light.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
State the cause of dispersion of white light
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Describe an activity to show that colours of white light splitted by a glass prism can be recombined to get white light by another identical glass prism. Also draw ray diagram to show the recombination of the spectrum of white light.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Water is an elixir of life, a very important natural resource. Your Science teacher wants you to prepare a plan for a formative assessment activity, "How to save water, the vital natural resource". Write any two ways that you will suggest to bring awareness in your neighbourhood, on 'how to save water'.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
Name and explain any one way by which the underground water table does not go down further.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
List three distinguishing features, in tabular form, between acquired traits and the inherited traits.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
With the help of suitable examples, explain why certain traits cannot be passed on to the next generation. What are such traits called?
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
List two functions ovary of human female reproductive system.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Write the function of the following part in a human female reproductive system:
Uterus
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Write the function of the following part in a human female reproductive system:
Fallopian tube
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Why are certain compounds called hydrocarbons? Write the general formula for homologous series of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes and also draw the structure of the first member of each series. Write the name of the reaction that converts alkenes into alkanes and also write a chemical equation to show the necessary conditions for the reaction to occur.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student suffering from myopia is not able to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 m. List two possible reasons due to which this defect of vision may have arisen. With the help of ray diagrams, explain
(i) why the student is unable to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 m from his eyes.
(ii) the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision and how this defect is corrected by the use of this lens.
(b) If, in this case, the numerical value of the focal length of the corrective lens is 5 m, find the power of the lens as per the new Cartesian sign convention
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations :
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –100 | +25 |
| 2 | –60 | +30 |
| 3 | –40 | +40 |
| 4 | –30 | +60 |
| 5 | –25 | +100 |
| 6 | –15 | +120 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason to justify your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of the observation which is not correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion?
(c) Select an appropriate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S.No. 2. Also find the approximate value of magnification.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always diminished, erect and virtual, state the type of the mirror and also draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Write one use such mirrors are put to and why.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Define the radius of curvature of spherical mirrors.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Find the nature and focal length of a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is +24 cm.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Advertisements
Study the following ray diagram:
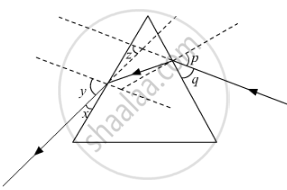
In this diagram, the angle of incidence, the angle of emergence and the angle of deviation respectively have been represented by
(A) y, p, z
(B) x, q, z
(C) p, y, z
(D) p, z, y
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
A student very cautiously traces the path of a ray through a glass slab for different values of the angle of incidence (∠i). He then measures the corresponding values of the angle of refraction (∠r) and the angle of emergence (∠e) for every value of the angle of incidence. On analysing these measurements of angles, his conclusion would be
(A) ∠i > ∠r > ∠e
(B) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
(C) ∠i < ∠r < ∠e
(D) ∠i = ∠e < ∠r
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

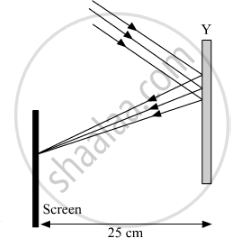
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A student obtains a blurred image of a distant object on a screen using a convex lens. To obtain a distinct image on the screen he should move the lens
(A) away from the screen
(B) towards the screen
(C) to a position very far away from the screen
(D) either towards or away from the screen depending upon the position of the object
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
While studying the saponification reaction, what do you observe when you mix an equal amount of colourless vegetable oil and 20% aqueous solution of NaOH in a beaker?
(A) The colour of the mixture has become dark brown
(B) A brisk effervescence is taking place in the beaker
(C) The outer surface of the beaker has become hot
(D) The outer surface of the beaker has become cold
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
When you add a few drops of acetic acid to a test-tube containing sodium bicarbonate powder, which one of the following is your observation?
(A) No reaction takes place
(B) A colourless gas with pungent smell is released with brisk effervescence
(C) A brown coloured gas is released with brisk effervescence
(D) Formation of bubbles of a colourless and odourless gas
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student requires hard water for an experiment in his laboratory which is not available in the neighbouring area. In the laboratory there are some salts, which when dissolved in distilled water can convert it into hard water. Select from the following groups of salts, a group, each salt of which when dissolved in distilled water will make it hard.
(A) Sodium chloride, Potassium chloride
(B) Sodium sulphate, Potassium sulphate
(C) Sodium sulphate, Calcium sulphate
(D) Calcium sulphate, Calcium chloride
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
To perform an experiment to identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed, first of all you require a dicot seed. Select dicot seeds from the following group:
Wheat, Gram, Maize, Pea, Barley, Ground-nut
(A) Wheat, Gram and Pea
(B) Gram, Pea and Ground-nut
(C) Maize, Pea and Barley
(D) Gram, Maize and Ground-nut
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
The following vegetables are kept in a basket :
Potato, Tomato, Radish, Brinjal, Carrot, Bottle-gourd
Which two of these vegetables correctly represent the homologous structures?
(A) Carrot and Tomato
(B) Potato and Brinjal
(C) Radish and Carrot
(D) Radish and Bottle-gourd
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Draw in sequence (showing the four stages), the process of binary fission in Amoeba.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
A student places a candle flame at a distance of about 60 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm and focuses the image of the flame on a screen. After that he gradually moves the flame towards the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-toward or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the image?
(b) How does the size of the image change?
(c) How does the intensity of the image change as the flame moves towards the lens?
(d) Approximately for what distance between the flame and the lens, the image formed on the screen is inverted and of the same size?
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Mention the essential material (chemicals) to prepare soap in the laboratory. Describe in brief the test of determining the nature (acidic/alkaline) of the reaction mixture of saponification reaction.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 10 Science with solutions 2016 - 2017
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 10 Science-2017 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Science, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 10.
How CBSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Science will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
