Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How did Mendel explain that it is possible that a trait is inherited but not expressed in an organism?
Solution
Some traits that are inherited may not express themselves. Such hidden traits are known as recessive traits. Mendel explained this phenomenon with the help of monohybrid cross. In a monohybrid cross performed by Mendel, tall plant was crossed with a dwarf plant which produced all tall plants in F1 progeny.
However, when these F1 tall plants were crossed with each other, 'dwarf' trait, which was not observed in the F1 generation, reappered in the F2 progeny.
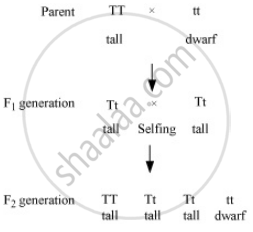
By this, it is concluded that dwarfness traits of parent pea plant were not lost. They were suppressed in the F1 generation by the tallness traits and reappeared in the F2 generation. So, we can say that a trait that is inherited may not be expressed in an organism.
RELATED QUESTIONS
A study found that children with light-coloured eyes are likely to have parents with light-coloured eyes. On this basis, can we say anything about whether the light eye colour trait is dominant or recessive? Why or why not?
Outline a project which aims to find the dominant coat colour in dogs.
How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word .
In pea plants, the gene for dwarfness is ..............whereas that for tallness is ............ .
For his experiments on heredity, Mendel used :
papaya plants
potato plants
pea plants
pear plants
The visible characteristic in an organism is known as :
(a) prototype
(b) stereotype
(c) phenotype
(d) genotype
A person first crossed pure-bred pea plants having round-yellow seeds with pure-bred pea plants having wrinkled-green seeds and found that only A-B type of seeds were produced in the F1 generation. When F1generation pea plants having A-B type of seeds were cross-bred by self-pollination, then in addition to the original round-yellow and wrinkled-green seeds, two new varieties A-D and C-B type of seeds were also obtained.
(a) What are A-B type of seeds?
(b) State whether A and B are dominant traits or recessive traits.
(c) What are A-D type of seeds?
(d) What are C-B type of seeds?
(c) Out of A-B and A-D types of seeds, which one will be produced in (i) minimum numbers, and (ii) maximum numbers, in the F2 generation?
The term 'father of genetics' is used for the scientist :
(a) Morgan
(b) Mendel
(c) Darwin
(d) Marie Curie
____________ refers to the transmission of genetic information from parental generation to next generation.
In the following figure showing a germinating gram seed, name the parts labelled as A, B and C:
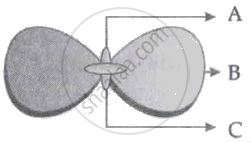
Why is Part 'B' considered to be important during germination?
