Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How did Mendel explain that it is possible that a trait is inherited but not expressed in an organism?
उत्तर
Some traits that are inherited may not express themselves. Such hidden traits are known as recessive traits. Mendel explained this phenomenon with the help of monohybrid cross. In a monohybrid cross performed by Mendel, tall plant was crossed with a dwarf plant which produced all tall plants in F1 progeny.
However, when these F1 tall plants were crossed with each other, 'dwarf' trait, which was not observed in the F1 generation, reappered in the F2 progeny.
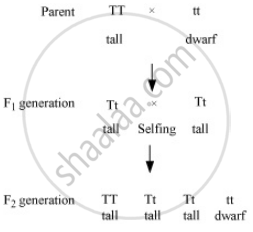
By this, it is concluded that dwarfness traits of parent pea plant were not lost. They were suppressed in the F1 generation by the tallness traits and reappeared in the F2 generation. So, we can say that a trait that is inherited may not be expressed in an organism.
संबंधित प्रश्न
A pea plant with blue colour flower denoted by BB is cross-bred with a pea plant with white flower denoted by ww.
(a) What is the expected colour of the flowers in their F1 progeny?
(b) What will be the percentage of plants bearing white flower in F2 generation, when the flowers of F1 plants were selfed?
(c) State the expected ratio of the genotype BB and Bw in the F2 progeny.
Name the information source for making proteins in the cells.
Mendel crossed tall pea plants with dwarf pea plants in his experiment. Write his observations giving reason on the F1 and F2 generations.
List any two contrasting characters other than height that Mendel used in his experiments in pea plants.
Using height (tallness/dwarfness) of a plant as an example, show that genes control the characteristics or traits in an organism.
What is the genotype of (i) dwarf plants, and (ii) tall plants, whose parental cross always produces tall offspring?
In order to ensure that he had pure-breeding plants for his experiments, Mendel :
(a) cross-fertilised each variety with each other
(b) let each variety self fertilise for several generations
(c) removed the female parts of the plants
(d) removed the male parts of the plants.
Pure-bred pea plants A are crossed with pure-bred pea plants B. It is found that the plants which look like A do not appear in F1 generation but re-emerge in F2 generation. Which of the plants A and B are : (i) tall, and (ii) dwarf? Give reason for your answer.
One of the following traits of the parents cannot be passed on to their future generations. This trait is :
(a) cleft chin
(b) pointed chin
(c) scarred chin
(d) broad chin
If we pure-bred tall (dominant) pea plant with pure-bred dwarf (recessive) pea plant we will get pea plants of F1 generation. If we now self-cross the pea plant of F1 generation, then we obtain pea plants of F2 generation.
(a) What do the plants of F2 generation look like?
(b) State the ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in F2 generation.
(c) State the type of plants not found in F1 generation but appeared in F2 generation, mentioning the reason for the same.
