Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How did Mendel explain that it is possible that a trait is inherited but not expressed in an organism?
उत्तर
Some traits that are inherited may not express themselves. Such hidden traits are known as recessive traits. Mendel explained this phenomenon with the help of monohybrid cross. In a monohybrid cross performed by Mendel, tall plant was crossed with a dwarf plant which produced all tall plants in F1 progeny.
However, when these F1 tall plants were crossed with each other, 'dwarf' trait, which was not observed in the F1 generation, reappered in the F2 progeny.
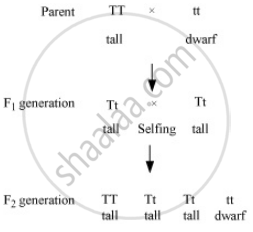
By this, it is concluded that dwarfness traits of parent pea plant were not lost. They were suppressed in the F1 generation by the tallness traits and reappeared in the F2 generation. So, we can say that a trait that is inherited may not be expressed in an organism.
संबंधित प्रश्न
How do Mendel’s experiments show that the traits may be dominant or recessive?
Mendel in one of his experiments with pea plants crossed a variety having round seed with one having wrinkled seeds. Write his observations, giving reasons, of F1 and F2 progeny
To perform an experiment to identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed, first of all you require a dicot seed. Select dicot seeds from the following group:
Wheat, Gram, Maize, Pea, Barley, Ground-nut
(A) Wheat, Gram and Pea
(B) Gram, Pea and Ground-nut
(C) Maize, Pea and Barley
(D) Gram, Maize and Ground-nut
State whether the following statement is true or false :
The sex of an infant is not a case of inheritance of characteristics.
In the human blood grouping, the four basic blood types are type A, type B, type AB, and type O. The blood proteins A and B are :
(a) simple dominant and recessive traits
(b) incomplete dominant traits
(c) codominant traits
(d) sex-linked traits
Pure-bred pea plants A are crossed with pure-bred pea plants B. It is found that the plants which look like A do not appear in F1 generation but re-emerge in F2 generation. Which of the plants A and B are : (i) tall, and (ii) dwarf? Give reason for your answer.
List two differences in tabular form between dominant trait and recessive traits. What percentage/proportion of the plants in the F2 generation/progeny were round, in Mendel's cross between round and wrinkled pea plants?
Explain the mechanism of hereditary changes.
Define Heredity. Give two examples.
In humans, if gene B gives brown eyes and gene b gives blue eyes, what will be the colour of eyes of the persons having combinations
(i) Bb and (ii) BB?
