Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the mechanism of hereditary changes.
उत्तर १
Hereditary changes can occur due to the following changes:
- Natural Selection: One allele is fixed for the population as it provides a survival advantage.
- Genetic Drift: Sudden change in a small population due to which genetic variability is reduced.
- Mutations: Sudden and inheritable changes in the genetic material that give rise to a new allele.
- Recombination: When the crossing over occurs during meiosis, the sequence of alleles changes on the chromosomes.
उत्तर २
The mechanism of hereditary changes is as follows:
- Diversity or hereditary changes occur due to genetic variation.
- In sexually reproducing organisms, a fusion of gametes from male and female parents occurs; the offspring always has recombined genes of both the parents. These offspring thus show some characters of either of the parents.
- Also, sometimes sudden changes known as mutations occur in the genes. A change in the position of even a single nucleotide can cause either a minor effect or a considerable alteration in the characters of an individual.
- If these changes (mutations) occur in the DNA of germline cells, then, these changes would be inherited to the next generation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define heredity.
A cross was made between pure breeding pea plants one with round and green seeds and the other with wrinkled and yellow seeds.
(a) Write the phenotype of F1 progeny. Give reason for your answer.
(b) Write the different types of F2 progeny obtained along with their ration when F1 progeny was selfed.
Name the information source for making proteins in the cells.
Outline a project which aims to find the dominant coat colour in dogs.
How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny?
To perform an experiment to identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed, first of all you require a dicot seed. Select dicot seeds from the following group:
Wheat, Gram, Maize, Pea, Barley, Ground-nut
(A) Wheat, Gram and Pea
(B) Gram, Pea and Ground-nut
(C) Maize, Pea and Barley
(D) Gram, Maize and Ground-nut
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding pea plants bearing violet flowers with pea plants bearing white flowers. What will be the result in F1 progeny?
Mendel said that the characteristics or traits of organisms are carried from one generation to the next by internal factors which occur in pairs. What is the modern name for these factors?
The gene for red hair is recessive to the gene for black hair. What will be the hair colour of a person if he inherits a gene for red hair from his mother and a gene for black hair from his father?
What will you get in the F1 and F2 generations in the following cross?
Pure tall pea plant × Pure dwarf pea plant
In the F2 generation of a cross, progeny having different traits are produced in the ratio 3 : 1. State whether it is a monohybrid cross or a dihybrid cross? Give one example of such a cross.
What is the genotype of (i) dwarf plants, and (ii) tall plants, whose parental cross always produces tall offspring?
What sizes of plants are produced if both parents have genes Tt?
Give the contrasting traits of the following characters in pea plant and mention which is dominant and which is recessive :
Round seed
State Mendel's second law of inheritance.
For his experiments on heredity, Mendel used :
papaya plants
potato plants
pea plants
pear plants
In the human blood grouping, the four basic blood types are type A, type B, type AB, and type O. The blood proteins A and B are :
(a) simple dominant and recessive traits
(b) incomplete dominant traits
(c) codominant traits
(d) sex-linked traits
In humans, if gene B gives brown eyes and gene b gives blue eyes. What will be the colour of eyes of the persons having the following combination of genes?
(a) Bb
(b) bb
(c) BB
Pure-bred pea plants A are crossed with pure-bred pea plants B. It is found that the plants which look like A do not appear in F1 generation but re-emerge in F2 generation. Which of the plants A and B are : (i) tall, and (ii) dwarf? Give reason for your answer.
What are the possible blood groups likely to be inherited by children born to a group A mother and a group B father? Explain your reasoning.
List two differences in tabular form between dominant trait and recessive traits. What percentage/proportion of the plants in the F2 generation/progeny were round, in Mendel's cross between round and wrinkled pea plants?
"It is possible that a trait is inherited but may not be expressed." Give a suitable example to justify this statement.
If we pure-bred tall (dominant) pea plant with pure-bred dwarf (recessive) pea plant we will get pea plants of F1 generation. If we now self-cross the pea plant of F1 generation, then we obtain pea plants of F2 generation.
(a) What do the plants of F2 generation look like?
(b) State the ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in F2 generation.
(c) State the type of plants not found in F1 generation but appeared in F2 generation, mentioning the reason for the same.
Mendel, in one of his experiments with pea plants, crossed a variety of pea plant having round seeds with one having wrinkled seeds. State Mendel’s observations giving reasons of F1 and F2 progeny of this cross. Also, list any two contrasting characters, other than round seeds of pea plants that Mendel used in his experiments.
Answer the following question.
Name the plant Mendel used for his experiment. What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F1 and F2 generations when he crossed the tall and short plants? Write the ratio he obtained in F2 generation plants.
What is genetics?
What will be the number of chromosomes present in each gamete produced by the plants if the palisade cells of a species of the plant contain 28 chromosomes in all?
In human males all the chromosomes are paired perfectly except one. This/these unpaired chromosome is/are
- large chromosome
- small chromosome
- Y-chromosome
- X-chromosome
In the following figure showing a germinating gram seed, name the parts labelled as A, B and C:
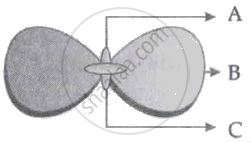
Why is Part 'B' considered to be important during germination?
A cross between pea plant with white flowers (vv) and pea plant with violet flowers (VV) resulted in F2 progeny in which ratio of violet (VV) and white (vv) flowers will be ______.
