Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define heredity.
What is heredity?
उत्तर १
Heredity is defined as the transfer of biological characters from one generation to another via genes.
उत्तर २
The transmission of characters from the parents to their offsprings is called heredity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How do Mendel's experiment show that traits are inherited independently?
In a monohybrid cross between tall pea plants (TT) and short pea plants (tt), a scientist obtained only tall pea plants (Tt) in the F1 generation. However, on selfing the F1 generation pea plants, he obtained both tall and short plants in F2 generation. On the basis of above observations with other angiosperms also, can the scientist arrive at a law? If yes, explain the law. If not, give justification for your answer.
What is a gene?
Mendel in one of his experiments with pea plants crossed a variety having round seed with one having wrinkled seeds. Write his observations, giving reasons, of F1 and F2 progeny
List any two contrasting characters other than roundness of pea plants that Mendel used in his experiments with pea plants.
How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny?
To perform an experiment to identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed, first of all you require a dicot seed. Select dicot seeds from the following group:
Wheat, Gram, Maize, Pea, Barley, Ground-nut
(A) Wheat, Gram and Pea
(B) Gram, Pea and Ground-nut
(C) Maize, Pea and Barley
(D) Gram, Maize and Ground-nut
What constitutes the link between one generation and the next?
Mendel said that the characteristics or traits of organisms are carried from one generation to the next by internal factors which occur in pairs. What is the modern name for these factors?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word .
In pea plants, the gene for dwarfness is ..............whereas that for tallness is ............ .
What will you get in the F1 and F2 generations in the following cross?
Pure tall pea plant × Pure dwarf pea plant
In the F2 generation of a cross, progeny having different traits are produced in the ratio 3 : 1. State whether it is a monohybrid cross or a dihybrid cross? Give one example of such a cross.
What is the genotype of dwarf plants which always produced dwarf offspring?
Gregor Mendel's first law of genetics states "Of a pair of contrasted characters, only one can be represented in a gamete by its internal 'factor' State where these factors are found in gametes.
What are the units of heredity.
Why did Mendel choose pea plants for conducting his experiments on inheritance?
State Mendel's second law of inheritance.
How do Mendel's experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
When two parents are crossed, the offspring are referred to as :
recessives
test cross
F1 generation
F2 generation
In order to ensure that he had pure-breeding plants for his experiments, Mendel :
(a) cross-fertilised each variety with each other
(b) let each variety self fertilise for several generations
(c) removed the female parts of the plants
(d) removed the male parts of the plants.
A pregnant woman has an equal chance of her baby being blood group A or blood group AB. Which one of the following shows the possible genotypes of the woman and the father of her child?
(a) IA IA and IB IO
(b) IA IB and IB IO
(c) IA IO and IB IO
(d) IA IB and IA IO
The following results were obtained by a scientist who crossed the F1 generation of pure-breeding parents for round and wrinkled seeds.
| Dominant trait | Recessive trait | No. of F2 offspring |
| Round seeds | Wrinkled seeds | 7524 |
From these results, it can be concluded that the actual number of round seeds he obtained was ______
A trait in an organism is influenced by ______
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) for every hormone there is a gene
(b) for every protein there is a gene
(c) for production of every enzyme there is a gene
(d) for every type of fat there is a gene
Pure-bred pea plants A are crossed with pure-bred pea plants B. It is found that the plants which look like A do not appear in F1 generation but re-emerge in F2 generation. Which of the plants A and B are : (i) tall, and (ii) dwarf? Give reason for your answer.
A red-haired woman marries a brown-haired man, and all the children are brown haired. Explain this genetically.
What are the possible blood groups likely to be inherited by children born to a group A mother and a group B father? Explain your reasoning.
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits-blood group A or O - is dominant? Why or why not?
Mendel first crossed pure-bred pea plants having round-yellow seeds with pure-bred pea plants having wrinkled-green seeds and found that only round-yellow seeds were produced in the F1 generation. When F1generation pea plants having round-yellow seeds were cross-bred by self pollination, then peas having round-yellow seeds, round green seeds, wrinkled-yellow seeds and wrinkled-green seeds were produced. Mendel collected a total of 2160 seeds.
(a) What will be the number of (i) round green seeds (ii) wrinkled green seeds (iii) round yellow seeds, and (iv) wrinkled-yellow seeds?
(b) Which 'ratio' as established by Mendel have you made use of in answering the part (a) above?
Pure-bred round-yellow pea seeds have genotype RRYY and the pure-bred wrinkled-green pea seeds have genotype rryy. Keeping this in mind, write the phenotypes of the following genotypes of hybrid pea seeds :
(a) Rryy
(b) rrYy
(c) rrYY
(d) RrYy
(e) RRyy
One of the following traits cannot be inherited. This one is :
(a) colour of eyes
(b) colour of skin
(c) size of body
(d) nature of hair
Only one of the following characteristic of the parents can be inherited by their children. This one is :
(a) deep scar on chin
(b) snub nose
(c) technique of swimming
(d) cut nose
List two differences in tabular form between dominant trait and recessive traits. What percentage/proportion of the plants in the F2 generation/progeny were round, in Mendel's cross between round and wrinkled pea plants?
If we pure-bred tall (dominant) pea plant with pure-bred dwarf (recessive) pea plant we will get pea plants of F1 generation. If we now self-cross the pea plant of F1 generation, then we obtain pea plants of F2 generation.
(a) What do the plants of F2 generation look like?
(b) State the ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in F2 generation.
(c) State the type of plants not found in F1 generation but appeared in F2 generation, mentioning the reason for the same.
Answer the following question.
Name the plant Mendel used for his experiment. What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F1 and F2 generations when he crossed the tall and short plants? Write the ratio he obtained in F2 generation plants.
Who is the pioneer of modern genetics?
In humans, if gene B gives brown eyes and gene b gives blue eyes, what will be the colour of eyes of the persons having combinations
(i) Bb and (ii) BB?
In the following Question, the Assertion and Reason have been put forward. Read the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
Assertion: When pure breed tall plants are crossed with pure breed short plants, all the plants in F1 progeny are tall. When the tall plants of F1 progeny are crossed, short plants re-appear in F2 progeny.
Reason: Traits are independently inherited.
If a round, green seeded pea plant (RR yy) is crossed with wrinkled, yellow seeded pea plant, (rr YY) the seeds produced in F1 generation are
If a tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf pea plant then, what percentage of F1 and F2 generation respectively will be tall?
In the following figure showing a germinating gram seed, name the parts labelled as A, B and C:
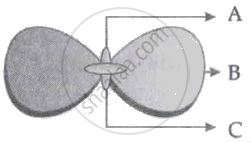
Why is Part 'B' considered to be important during germination?
Name the following:
The basic units of heredity.
Rewrite the correct form of the statement by changing the first or last word only:
The inheritable feature of an organism is termed as heredity.
