Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
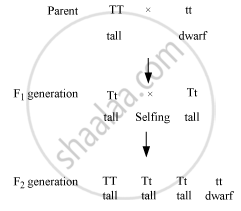
If we pure-bred tall (dominant) pea plant with pure-bred dwarf (recessive) pea plant we will get pea plants of F1 generation. If we now self-cross the pea plant of F1 generation, then we obtain pea plants of F2 generation.
(a) What do the plants of F2 generation look like?
(b) State the ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in F2 generation.
(c) State the type of plants not found in F1 generation but appeared in F2 generation, mentioning the reason for the same.
उत्तर
When a pure breeding tall pea plant is crossed with a pure breeding dwarf pea plant
(a) All the plants in the F1 generation appear tall.
(b) The ratio of tall pea plant to dwarf pea plants is 3 (tall) : 1 (dwarf).
(c) The dwarf plant does not appear in the F1 generation but appears in the F2 generation because the progeny produced in the F1generation were heterozygous (Tt). Hence, when they were selfed for obtaining the F2 generation, dwarf plants were also formed in the progeny. The cross involved in as follows
संबंधित प्रश्न
A pea plant with blue colour flower denoted by BB is cross-bred with a pea plant with white flower denoted by ww.
(a) What is the expected colour of the flowers in their F1 progeny?
(b) What will be the percentage of plants bearing white flower in F2 generation, when the flowers of F1 plants were selfed?
(c) State the expected ratio of the genotype BB and Bw in the F2 progeny.
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits – blood group A or O – is dominant? Why or why not?
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding pea plants bearing violet flowers with pea plants bearing white flowers. What will be the result in F1 progeny?
What constitutes the link between one generation and the next?
Name the scientist who gave the laws of inheritance.
It it an example of monohybrid cross or dihybrid cross?
If the ratio of each phenotype of the seeds of pea plants in the F2 generation is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1, it is known as :
(a) tetrahybrid ratio
(b) monohybrid ratio
(c) dihybrid ratio
(d) trihybrid ratio
Hereditary characters are transferred from parents to offspring by ______ hence they are said to be structural and functional units of heredity.
What is genetics?
Who is the pioneer of modern genetics?
