Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
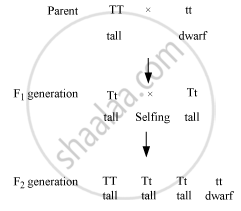
If we pure-bred tall (dominant) pea plant with pure-bred dwarf (recessive) pea plant we will get pea plants of F1 generation. If we now self-cross the pea plant of F1 generation, then we obtain pea plants of F2 generation.
(a) What do the plants of F2 generation look like?
(b) State the ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in F2 generation.
(c) State the type of plants not found in F1 generation but appeared in F2 generation, mentioning the reason for the same.
Solution
When a pure breeding tall pea plant is crossed with a pure breeding dwarf pea plant
(a) All the plants in the F1 generation appear tall.
(b) The ratio of tall pea plant to dwarf pea plants is 3 (tall) : 1 (dwarf).
(c) The dwarf plant does not appear in the F1 generation but appears in the F2 generation because the progeny produced in the F1generation were heterozygous (Tt). Hence, when they were selfed for obtaining the F2 generation, dwarf plants were also formed in the progeny. The cross involved in as follows
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define heredity.
List any two contrasting characters other than roundness of pea plants that Mendel used in his experiments with pea plants.
A study found that children with light-coloured eyes are likely to have parents with light-coloured eyes. On this basis, can we say anything about whether the light eye colour trait is dominant or recessive? Why or why not?
In the F2 generation of a cross, progeny having different traits are produced in the ratio 3 : 1. State whether it is a monohybrid cross or a dihybrid cross? Give one example of such a cross.
How do Mendel's experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
When two parents are crossed, the offspring are referred to as :
recessives
test cross
F1 generation
F2 generation
In order to ensure that he had pure-breeding plants for his experiments, Mendel :
(a) cross-fertilised each variety with each other
(b) let each variety self fertilise for several generations
(c) removed the female parts of the plants
(d) removed the male parts of the plants.
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits-blood group A or O - is dominant? Why or why not?
Explain the mechanism of hereditary changes.
A cross between pea plant with white flowers (vv) and pea plant with violet flowers (VV) resulted in F2 progeny in which ratio of violet (VV) and white (vv) flowers will be ______.
