Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation
Solution

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
To find the image-distance for varying object-distances in case of a convex lens, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object placed very far from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image of the screen.
(a) In which direction – towards or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) What happens to the size of image – does it increase or decrease?
(c) What happen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
"A lens can form a magnified erect image as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." State the nature of this lens and draw ray diagrams to justify the above statement. Mark the positions of O, F and 2F in the diagram.
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed in front of a convex lens between focus and optical centre. State three characteristics of the image formed.
What type of images can a convex lens make?
How would a pencil look like if you saw it through How would a pencil look like if you saw it through
An image formed on a screen is three times the size of the object. The object and screen are 80 cm apart when the image is sharply focussed.
State which type of lens is used.
Study the diagram given below.
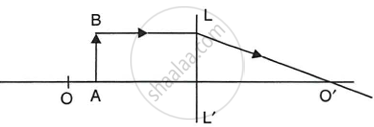
- Name the lens LL’.
- What are the points O and O’ called?
- Complete the diagram to form the image of the object AB.
- State the three characteristics of the image.
- Name a device in which this action of lens is used.
State two applications of a convex lens.
Yesh find out F1 and F2 of symmetric convex lens experimentally then which conclusion is true.
Draw neat diagram to show the
Convergent action of a convex lens,
