Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
To find the image-distance for varying object-distances in case of a convex lens, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object placed very far from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image of the screen.
(a) In which direction – towards or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) What happens to the size of image – does it increase or decrease?
(c) What happen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
Solution
(a) As the student moves the object towards the lens, the position of the image shifts away from the lens. To obtain a sharp image, he should move the screen away from the lens.
(b) The size of the image increases when the object is moved near the lens.
(c) When the object is placed very close to the lens, it can be considered to be placed between the focus and the optical centre. In this case, the image formed is virtual, erect and enlarged.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State any two uses of convex lenses.
With the help of a labelled diagram explain how a convex lens converges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the convex lens on the diagram.
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
Complete the following sentence.
A long-sighted person cannot see ........... objects clearly. Long-sightedness can be corrected by using .............. lenses.
Study the diagram below.
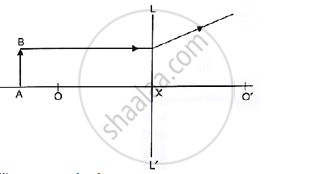
what are the points O, O’ called?
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used in cine projector.
An object is placed in front of a convex lens such that the image formed has the same size as that of the object. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this.
Diagram shows an object AB placed on the principal axis B of a convex lens placed in air. F1 and F2 are the two foci of the lens.
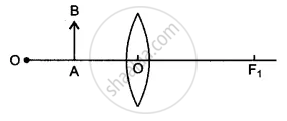
(i) Copy the diagram:
Draw a ray of light starting from B and passing through O. Show the same ray after refraction by the lens. Draw another ray from B which passes through F2 after refraction by the lens. Locate the final image
(ii) Is the image real or virtual?
Write scientific reason.
Adults need bifocal lens spectacle.

The above image shows a thin lens with a focal length of 5m.
- What is the kind of lens shown in the above figure?
- If a real inverted image is to be formed by this lens at a distance of 7m from the optical centre, then show with calculation where should the object be placed.
- Draw a neatly labelled diagram of the image formation mentioned in (ii).
