Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the above two cases illustrates the working of a magnifying glass?
Solution
Case (b) illustrates the working of magnifying lens as the object is between the focus and optical centre.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
To find the image-distance for varying object-distances in case of a convex lens, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object placed very far from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image of the screen.
(a) In which direction – towards or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) What happens to the size of image – does it increase or decrease?
(c) What happen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at 90° (that is, perpendicular to the glass block)
If an object is placed at the focus of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What would be the image distance if the object distance was 90 cm?
How would a pencil look like if you saw it through How would a pencil look like if you saw it through
What type of lens is used to correct
hypermetropia
A pin 2 cm long is placed 12 cm away from a convex lens at right angles to the principal axis. If the focal length of the lens is 20 cm, by scale drawing find the size of the image and its magnification.
What is the difference between a double convex and a bi-convex lens?
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of photographic camera.
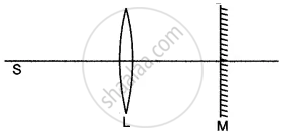
In the figure given below L is a convex lens, M is a plane mirror and S is a point source of light. Rays of light from the source S return to their point of origin. Complete the ray diagram to show this. What is the point S called?