Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In Myopia the human eye _______.
Options
cannot see nearby objects distinctly
cannot see distant objects clearly
cannot see nearby as well as distant objects clearly
can see nearby as well as distant objects clearly
Solution
In Myopia the human eye cannot see distant objects clearly.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Given below is a diagram showing a defect of human eye. Study it and answer the following questions.
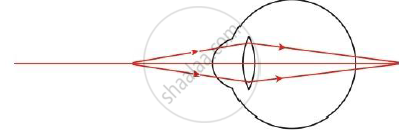
(i) Name the defect shown in the figure.
(ii) Give reason for this defect of eye in human being.
(iii) Name the type of lens used to correct the eye defect.
List three common refractive defects of vision. Suggest the way of correcting these defects.
What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
The kind of lens required to correct Myopia
What is the scientific name of
long-sightedness?
Name any two defects of vision which can be corrected by using spectacles.
Name one defect of vision (or eye) which cannot be corrected by any type of spectacle lenses.
A man can read the number of a distant but clearly but he finds difficulty in reading a book.
What type of spectacle lens should he use to correct the defect?
Name the defect of vision which can be corrected by a converging lens. Show clearly by a ray diagram how the lens corrects the defect.
Explain with the help of labelled ray diagram, the defect of vision called myopia and how it is corrected by a lens.
Explain with the help of labelled ray-diagram, the defect of vision called hypermetropia, and hot it is corrected by a lens.
A person suffering from the eye-defect myopia (short-sightedness) can see clearly only up to a distance of 2 metres. What is the nature and power of lens required to rectify this defect?
The near-point of a person suffering from hypermetropia is at 50 cm from his eye. What is the nature and power of the lens needed to correct this defect? (Assume that the near-point of the normal eye is 25 cm).
What is long-sightedness? State the two causes of long-sightedness (or hypermetropia). With the help of ray diagrams, show:
(i) the eye-defect long-sightedness.
(ii) correction of long-sightedness by using a lens.
The picture given here shows a person wearing 'half-moon' spectacles. What sort of eye-defect do do you think he has? Why are these particular spectacles useful to him?
To read a book held at a distance of 25 cm, will she need converging or diverging spectacle lenses?
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in the bracket.
Rods and cones (sensitivity).
Name an old age eye defect. What happens in it?
Describe the mechanism of focusing the image of a distant object in your eye when you raise your head after reading a book.
A person cannot read newspaper placed nearer than 50 cm from his eyes. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this defect. List its two possible causes. Draw a ray diagram to show how this defect may be corrected using a lens of appropriate focal length.
State one role of ciliary muscles in the human eye.
Choose the correct answer :
Presbyopia is a disease of _____________
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye? Study the same and answer the question that follow :
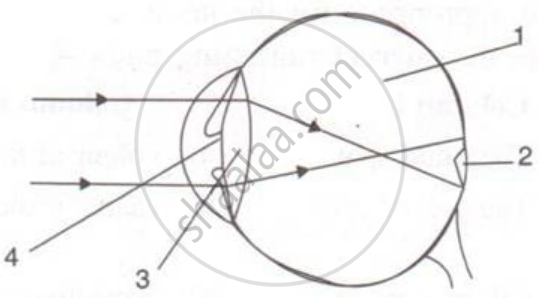
Name the type of lens used to correct this eye defect.
Name the common defects of the eye.
Give Reason:
Why do we see clearly in the central region of the retina?
Give Reason:
Deficiency of vitamin A causes night blindness.
Explain the Term: Presbyopia
What type of lens is used to correct Hypermetropia?
Myopia may arise due to ____________.
A person needs a lens of power –4.5 D for correction of her vision.
- What kind of defect in vision is she suffering from?
- What is the focal length of the corrective lens?
- What is the nature of the corrective lens?
Correlate the given sequence:
Hypermetropia : Convex lens : ______ : Concave lens
Observe the figure whether it is correct or not and explain the phenomenon.
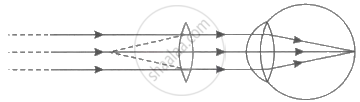
Observe the following diagram and answer questions following it:

- Identify the defect of vision shown.
- List its two causes.
- Name the type of lens used for the correction of this defect.
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e. Power of accommodation |
Given alongside is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
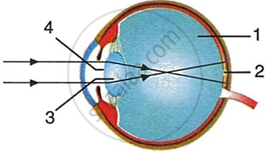 |
- Name the defect shown in the diagram.
- Give two possible reasons for this defect.
- Name the parts labelled 1 to 4.
- Name the type of lens used to correct this eye defect.
- Draw a labelled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified using the lens named above.
