Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If the monopolist firm of Exercise 3, was a public sector firm. The government set a rule for its manager to accept the government fixed price as given (i.e. to be a price taker and therefore behave as a firm in a perfectly competitive market). And the government decide to set the price so that demand and supply in the market are equal. What would be the equilibrium price, quantity and profit in this case?
Solution
If the government sets a rule for the public sector firm to accept the fixed price, then, the monopoly firm will have to behave like a perfectly competitive firm and will be a price taker. In this case, the price fixed (Pe), as set by the government, will equate the demand and the supply, which will determine the equilibrium point ‘E’. At the price Pe, the firm earns normal profit, i.e. zero economic profit.
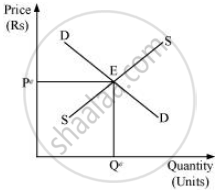
Equilibrium price = Pe (fixed by the government)
Equilibrium quantity = Qe
Profit = Normal profit
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A monopoly firm has a total fixed cost of Rs 100 and has the following demand schedule:
|
Quantity |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
Price |
100 |
90 |
80 |
70 |
60 |
50 |
40 |
30 |
20 |
10 |
Findthe short run equilibrium quantity, price and total profit. What would be the equilibrium in the long run? In case the total cost is Rs 1000, describe the equilibrium in the short run and in the long run.
The market demand curve for a commodity and the total cost for a monopoly firm producing the commodity is given in the schedules below.
|
Quantity |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
Price |
52 |
44 |
37 |
3 |
26 |
22 |
19 |
16 |
13 |
|
Quantity |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
Total Cost |
10 |
60 |
90 |
100 |
102 |
105 |
109 |
115 |
125 |
Use the information given to calculate the following:
(a) The MR and MC schedules
(b) The quantities for which MR and MC are equal
(c) The equilibrium quantity of output and the equilibrium price of the commodity
(d) The total revenue, total cost and total profit in the equilibrium
Will the monopolist firm continue to produce in the short run if a loss is incurred at the best short run level of output?
Explain why the demand curve facing a firm under monopolistic competition is negatively sloped.
What is the reason for the long run equilibrium of a firm in monopolistic competition to be associated with zero profit?
