Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Explain in brief the reason for the following:
Twinkling of stars
What is the reason for twinkling of stars?
Solution 1
Light coming from the stars undergoes refraction on entering the Earth’s atmosphere. This refraction continues until it reaches the Earth’s surface. This happens because of the temperature variation of atmospheric air. Hence, the atmospheric air has a changing refractive index at various altitudes. In this case, light from the stars continuously travels from a rarer medium to a denser medium. Hence, it continuously bends towards the normal.
The refractive index of air medium gradually increases with a decrease in altitude. The continuous bending of starlight towards the normal results in a slight rise in the apparent position of the star.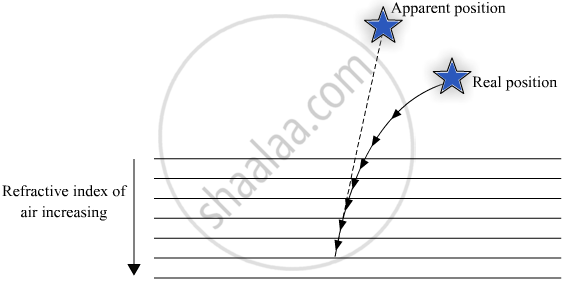
Since the physical conditions of the Earth’s atmosphere keep changing, the apparent position of the star is not stationary. The star changes its position continuously, which makes it twinkle. This happens because light from the stars travels a very large distance before reaching the observer. However, the path varies continuously because of uneven atmospheric conditions. Hence, the stars seem to be fluctuating, sometimes appearing bright and sometimes dull. All this, together, causes the twinkling of stars.
Solution 2
The twinkling of stars is caused by atmospheric refraction of starlight. The starlight passes through different layers of the Earth's atmosphere, which have varying densities. This bending of light makes the stars appear to twinkle.
Notes
Students can refer to the provided solutions based on their preferred marks.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why does the sun seem to rise two minutes before the actual sunrise and set two minutes after the actual sunset ? Explain with the help of labelled diagram.
What colours make up white light?
Give the meaning of the term VIBGYOR. With which phenomenon is it connected?
What is the colour of the sunlight:
scattered by the dust particles in the atmosphere?
Which component of sunlight is scattered away when the sun appears red at sunrise or sunset?
Sunset is red because at that time the light coming from the sun has to travel:
(a) lesser thickness of earth's atmosphere
(b) greater thickness of earth's atmosphere
(c) varying thickness of earth's atmosphere
(d) along the horizon
How would the sky appear when seen from the space (or moon)? Give reason for your answer.
Describe an experiment to show that “sunlight is essential for photosynthesis”.
Draw a labelled diagram to show (i) reddish appearance of the sun at the sunrise or the sunset and (ii) white appearance of the sun at noon when it is overhead.
Why is the colour of the clear sky blue?
