Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the problem of what to produce.
Solution
What to produce refers to the selection of the goods and the quantity to be produced of each selected commodity. This problem arises because resources are scarce and have alternative uses. As many goods can be produced from these resources, the problem is that which of the goods should be produced.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain, with reasons, whether you Agree or Disagree with the following statement
There are no exceptions to the Law of Demand.
Demand deposits include (choose the correct alternative)
(a) Saving account deposits and fixed deposits
(b) Saving account deposits and current account deposits
(c) Current account deposits and fixed deposits
(d) All types of deposits
Fill in the blank using proper alternative given in the bracket:
Perfectly inelastic demand curve is.....................................................
State whether the following statement is True or False :
Demand for necessary goods is inelastic.
(b) less elastic demand
(c) zero elastic demand
(d) unitary elastic demand
fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given in the bracket:
Demand for salt is ___________.
Write answers in ‘one’ or ‘two’ paras each.
What are the main determinants of aggregate demand?
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE
When demand increases, the demand curve shifts to the left.
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE
Individual demand is a demand by single buyer.
Answer the following question
What do you mean by demand?
Do you agree with the following statement? Give reason
Many factors influence the demand for a commodity.
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Utility | (a) Bread and butter |
| (2) Normal Goods | (b) Rise in price |
| (3) Contraction in demand | (c) Capacity of a commodity to satisfy human wants. |
| (4) Complementary goods | (d) Positively related |
If the increase in demand is greater than the increase in supply, then equilibrium price will ______
The demand curve of a firm under monopoly is ______
Identify the correctly matched pair of the items in Column A to that of Column B.
| Column A | Column B | ||
| (1) | Increase in demand for goods | (a) | Leftward shift in the demand curve |
| (2) | Decrease in demand | (b) | Perfectly Elastic Demand |
| (3) | Ed = ∞ | (c) | Increases in the income of the consumer |
| (4) | Downward Sloping | (d) | Income elasticity of Demand |
Assertion (A): Demand deposits are not legal tenders.
Reason (R): They are with the bank, so only can be used as a legal tender when cheques are issued for the transfer.
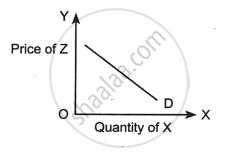
The figure given below shows the relation between the quantity demanded for the good X and the price of the good Z. What type of goods are X and Z?