Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain refraction of light on the basis of wave theory. Hence prove the laws of refraction
Solution
Laws of refraction :
The ratio of the velocity of light in rarer medium to the velocity of light in a denser medium is a constant called the refractive index of denser medium w.r.t. rarer medium. The incident rays, refracted rays, and normal lie in the same plane. Incident ray and refracted ray lie on opposite sides of normal.
Explanation :
Phenomenon of refraction can be explained on the basis of wave theory of light.
- Let XY be the plane refracting surface separating two media air and glass of respectively. indices μ1 and μ2 refractive.
- A plane wave front AB is advancing obliquely towards XY from the air. It is bounded by rays AA1 and BB1 which are incident rays.
- When ‘A’ reaches ‘A1’, then ‘B’ will be at ‘P’. It still has to cover distance PB1 to reach XY.
- According to Huygens’ principle, secondary wavelets will originate from A1 and will spread over a hemisphere in the glass.
- All the rays between AA1 and BB1 will reach XY and spread over the hemispheres of increasing radii in the glass. The surface of the tangency of all such hemispheres is RB1.
This gives rise to refracted wavefront B1R in the glass. - A1R and B1R1 are refracted rays.
- Let c1 and c2 be the velocities of light in air and glass respectively.
- At any instant of time ‘t’, distance covered by incident wavefront from P to B1 = PB1 = c1t Distance covered by a secondary wave from A1 to R = A1R = c2t.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Determine the change in wavelength of light during its passage from air to glass. If the refractive index of glass with respect to air is 1.5 and the frequency of light is 3.5 x 1014 Hz, find the wave number of light in glass.
[Velocity of light in air c = 3 x 108 m/s]
(a) A ray of light is incident normally on the face AB of a right-angled glass prism of refractive index aμg 1.5. The prism is partly immersed in a liquid of an unknown refractive index. Find the value of the refractive index of the liquid so that the ray grazes along the face BC after refraction through the prism.
(b) Trace the path of the rays if it were incident normally on the face AC.
At point A on the earth's surface the angle of dip, d = +25°. At a point Bon the earth's surface the angle of dip, d = −25°. We can interpret that
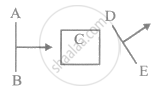
A wavefront AB passing through a system C emerges as DE. The system C could be:
Which of the following is conserved when light wave interfere?
Light travel faster in air than in glass according to
A Prism has reflecting angle of 60° when a ray is incident at 50° it suffer minimum deviation (Sm). The value of Sm is
If the critical angle for total internal reflecting from medium to vacuum is 30, the velocity of light n the medium is
A piano convex lens is made of refractive index 1.6. The radius of curvature of the curved surface is 60 cm. The focal length of the lens is
