Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Explain the structure of Fiber Optic Cable.
Explain Fiber-optic Cable with a neat diagram
Solution
(1) The light wave can be efficiently conducted through transparent glass fiber cables known as optic fiber cables.
(2) The centre conductor of this cable is a fibre that consists of highly refined glass or plastic.
(3) It is designed to transmit light signals with little loss.
(4) The fibre is coated with cladding or gel that reflects signals back into fibre to reduce signal loss. A plastic sheet protects the fibre from damage.
(5) The fibre optic cable is shown in the following figure.
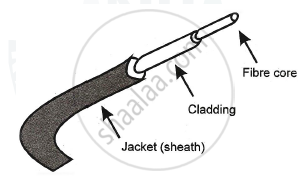
(6) The fibre optic cable is used in the optical transmission system.
(7) This cable has the extremely high bandwidth. It has zero sensitivity to EMI and runs over several kilometres.
(8) The characteristics of fibre optic cable are given below
- Cost: The cost of fibre optic cable is more than that of coaxial cable and Twisted pair cable.
- Installation: Fibre optic cable requires skilled installation. Every cable has minimum bend radius. They may get damaged if bent sharply Fibre optic cable cannot be stretched.
- Capacity: Fibre optic cable supports high data rates (up to 2,00,000 MBPS), even with long-run cables. Fibre optic cable can transmit 100 MBPS for several kilometres.
- Attenuation: Attenuation for fibre optic cable is much lower than co-axial cable and twisted pair cable. It can run to the larger distance.
- EMI: Fibre optic cable does not use electrical signals to transmit data, therefore they are free from EMI. The data transfer in fibre optic cable has high security, as it can not be detected by electronic wave dropping equipment.
