Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the equivalent resistance of a parallel resistor network.
Solution
Resistors are in parallel when they are connected across the same potential difference as shown in the following figure.
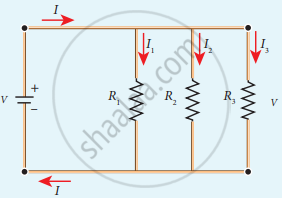
Three resistors in parallel
In this case, the total current I that leaves the battery in split into three separate paths. Let I1, I2 and I3 be the current through the resistors R1, R2 and R3 respectively. Due to the conservation of charge, total current in the circuit I is equal to sum of the currents through each of the three resistors.
I = I1 + I2 + I3 ……. (1)
Since the voltage across each resistor is the same, applying Ohm’s law to each resistor, we have
`"I"_1 = "V"/"R"_1, "I"_2 = "V"/"R"_2, "I"_1 = "V"/"R"_3`
Substituting these values in equation (1), we get
I = `"V"/"R"_1 + "V"/"R"_2 + "V"/"R"_3`
= V`[1/"R"_1 + 1/"R"_2 + 1/"R"_3]`
I = `"V"/"R"_"p"`
`1/"R"_"p" = 1/"R"_1 + 1/"R"_2 + 1/"R"_3`
Here RP is the equivalent resistance of the parallel combination of the resistors. Thus, when a number of resistors are connected in parallel, the sum of the reciprocal of the values of resistance of the individual resistor is equal to the reciprocal of the effective resistance of the combination as shown in the following figure.
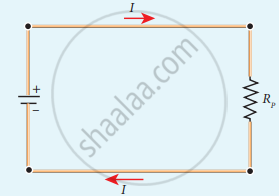
Equivalent resistance (RP) has the same current
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Is Ohm’s law universally applicable for all conducting elements? If not, give examples of elements which do not obey Ohm’s law.
Write the SI unit of resistivity
The graph between V and I for a conductor is a straight line passing through the origin.
Which law is illustrated by such a graph?
How should the two resistances of 2 ohms each be connected so as to produce an equivalent resistance of 1 ohm?
What is meant by the drift speed of free electrons?
Rewrite the following statement by selecting the correct option.
The S.I. unit of resistance is __________.
What is non-ohmic resistor?
A wire connected to a power supply of 230 V has power dissipation P1. Suppose the wire is cut into two equal pieces and connected parallel to the same power supply. In this case, power dissipation is P2. The ratio of `"P"_2/"P"_1` is
A current of 2amp flowing through a conductor produced 80 joule of heat in 10 sec. The resistance of the conductor is:-
