Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the following.
The atomic radii of Cl, I, and Br are 99, 133, and 114 pm, respectively.
Solution
- Cl, I and Br belong to group 17 (halogen group) in the periodic table.
- As we move down the group from top to bottom in the periodic table, a new shell gets added to the atom of the elements.
- As a result, the effective nuclear charge decreases due to an increase in the atomic size as well as an increased shielding effect.
- Therefore, the valence electrons experience less attractive force from the nucleus and are held less tightly resulting in the increased atomic radius.
- Thus, their atomic radii increase in the following order down the group.
Cl (99 pm) < Br (114 pm) < I (133 pm)
Hence, the atomic radii of Cl, I, and Br are 99, 133, and 114 pm, respectively.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the following.
The ionic radii of FΘ and Na⊕ are 133 and 98 pm, respectively.
Explain the following.
13Al is a metal, 14Si is a metalloid and 15P is a nonmetal.
Explain the following.
Cu forms coloured salts while Zn forms colourless salts.
Answer the following.
Why the second ionization enthalpy is greater than the first ionization enthalpy?
Answer the following.
Explain electronegativity and electron gain enthalpy. Which of the two can be measured experimentally?
Choose the correct option.
Consider the elements B, Al, Mg, and K predict the correct order of metallic character:
Choose the correct option.
The lanthanides are placed in the periodic table at
Answer the following question.
For the following pair, indicate which of the two species is of large size:
Fe2+ or Fe3+
With the help of a diagram answer the questions are given below:
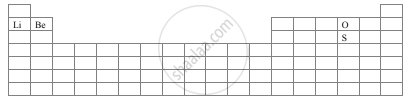
- Which atom should have smaller ionization energy, oxygen, or sulphur?
- The lithium forms +1 ions while beryllium forms +2 ions?
Define ionic radius
Define electronegativity
What are the valence electrons?
Define ionization enthalpy.
Name the factors on which ionization enthalpy depends?
How does ionization enthalpy vary down the group and across a period?
How the atomic size vary in a group and across a period? Explain with suitable example.
Give reason.
Alkali metals have low ionization enthalpies.
Give reason.
Inert gases have exceptionally high ionization enthalpies.
Give reason.
Fluorine has less electron affinity than chlorine.
