Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
| Fertilisation is the key process in sexually reproducing organisms and it acts as a vital link between two generations. Flowering plants adopt a unique pattern of sexual reproduction as compared to other organisms. |
- Explain the process of fertilisation in angiosperms.
- What is the precise location and function of filiform apparatus in the embryo sac of angiosperms?
- Fruits and seeds are generally formed due to fertilisation. Name the process involved in the production of the following without fertilisation:
- Fruits
- Seeds
Solution
-
Angiosperms, or flowering plants, have a unique fertilisation process known as double fertilisation, which begins when a pollen grain reaches the female stigma. The pollen tube discharges two sperm cells. Two polar nuclei combine to form a secondary nucleus, which then merges with one sperm nucleus from the pollen tube to generate an endosperm cell. The other sperm nucleus enters the egg cell with the help of synergids, degenerates and fuses with the nucleus.
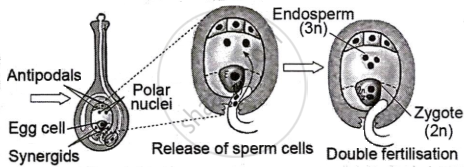
- The filiform apparatus is a thickened structure located at the embryo sac's micropylar end, also known as the megasporangium. The filiform apparatus guides pollen tubes into the synergids and releases male gametes
- Fruits: Parthenocarpy is the process of generating fruit without fertilisation.
- Seeds: Apomixis is the process of creating seeds without fertiliser.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the significance of meiocytes in a diploid organism.
The terms homothallic and monoecious are used to denote ______.
Fusion of unrelated gametes is called ______.
Development of an egg without fertilization is called ______.
Which is correct?
In oogamy, fertilization involves ______.
Which of the followings are monoecious and dioecious organisms?
| a. | Earthworm | ______ |
| b. | Chara | ______ |
| c. | Marchantia | ______ |
| d. | Cockroach | ______ |
In haploid organisms that undergo sexual reproduction, name the stage in the life cycle when meiosis occurs. Give reasons for your answer.
Do all the gametes formed from a parent organism have the same genetic composition (identical DNA copies of the parental genome)? Analyse the situation with the background of gametogenesis and provide or give suitable explanation.
Define perisperm.
