Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
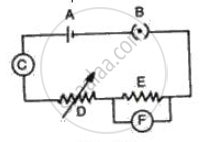
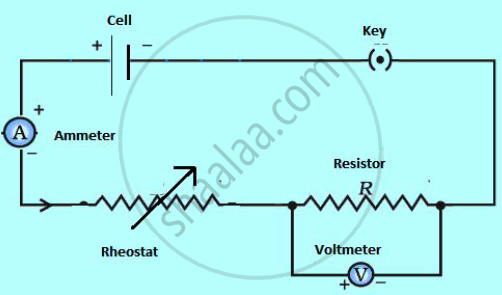
Fig. represents the circuit used for the verification of ohm's law. Label the different parts from A and F. State the function of each.
Solution
Functions:
(A) Cell- It provides the potential difference in the circuit.
(B) Key- It serves as a switch in the circuit. It supplies or cuts off current as required.
(C) Ammeter - It measures the current in the circuit.
(D) Rheostat- It helps to change the resistance of the circuit without changing its voltage.
(E) Resistor- It provides a constant resistance in the circuit.
(F) Voltmeter - It measure the potential drop across the resistor.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the unit of electrical resistance and give its symbol.
The unit of electrical resistance is:
(a) ampere
(b) volt
(c) coulomb
(d) ohm
The graph between V and I for a conductor is a straight line passing through the origin.
Which law is illustrated by such a graph?
State Ohm’s law and draw a neat labelled circuit diagram containing a battery, a key, a voltmeter, an ammeter, a rheostat and an unknown resistance to verify it.
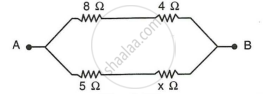
In the circuit shown below in Fig, calculate the value of x if the equivalent resistance between A and B is 4 Ω.
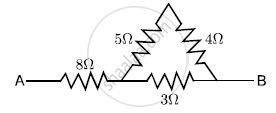
Calculate the effective resistance across AB?
State the relation correlating the electric current flowing in a conductor and the voltage applied across it. Also, draw a graph to show this. relationship.
State macroscopic form of Ohm’s law.
The resistance of a nichrome wire at 0°C is 10Ω. If its temperature coefficient of resistivity of nichrome is 0.004/ °C, find its resistance of the wire at boiling point of water. Comment on the result.
The unit of specific resistance is ____________.
