Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Figure shows a brick of weight 2 kgf and dimensions 20 cm x 10 cm × 5 cm placed in three different positions on the ground. Find the pressure exerted by the brick in each case.
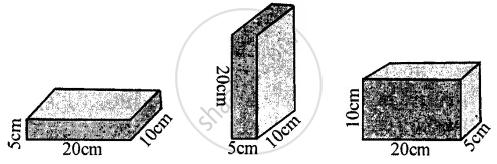
Solution
(a) Weight of bricks = Thrust = F = 2 kgf
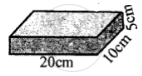
Area of base = `20/100 xx 10/100 = 1/50 "m"^2`
Pressure exerted P = `"F"/"A" = "2 kgf"/(1/50 "m"^2) = 100 "kgf m"^-2`
Or
Area of base = area of top L × B
20 cm × 10 = 200 cm2
P = `"Thrust"/"A" = "2 kgf"/200 "cm"^2 = 1/100 = 0.01 "kgf cm"^-2`
(b)
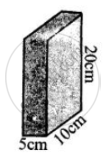
area of base = area of top
= 5 cm × 10 cm = 50 cm2
Pressure exerted = P = `"F"/"A" = "2 kgf"/"50 cm"^2 = 0.04`
P = 0.04 kgf cm-2
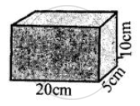
(c) Weight of brick
F = 2 kgf
Area of base = L × B
= 20 cm × 5 cm = 100 cm2
Pressure exerted = `"F"/"A" = 2/100 = 0.02 "kgf cm"^-2 `
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A 50 kg girl wearing high heel shoes balances on a single heel. The heel is circular with a diameter 1.0 cm. What is the pressure exerted by the heel on the horizontal floor?
Toricelli’s barometer used mercury. Pascal duplicated it using French wine of density 984 kg m–3. Determine the height of the wine column for normal atmospheric pressure.
A body weighing 5 kgf, placed on a surface of area 0.1 m2, exerts a thrust on the surface equal to
How much thrust will be required to exert a pressure of 20,000 Pa on an area of 1 cm2.
The pressure in a liquid at two points in the same horizontal plane are equal. Consider an elevator accelerating upward and a car accelerating on a horizontal road. The above statement is correct in
Multiple Choice Question.
A hydraulic lift is designed to lift heavy objects of maximum mass 2000 kg. The area of cross-section of piston carrying the load is 2.25 × 10-2 m2. What is the maximum pressure the smaller piston would have to bear?
A brick is kept in three different ways on a table as shown in figure. The pressure exerted by the brick on the table will be
 |
 |
 |
| (A) | (B) | (C) |
Fluids in general are ______.
All flowing substances, both liquids, and gases are called ______.
Assertion (A): Wide wooden sleepers are kept below railway lines to reduce pressure on the railway tracks and prevent them from sinking into the ground.
Reason (R): Pressure is directly proportional to the area in which it is acting.
