Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Figure shows a smooth pair of thick metallic rails connected across a battery of emf εhaving a negligible internal resistance. A wire ab of length l and resistance r can slide smoothly on the rails. The entire system lies in a horizontal plane and is immersed in a uniform vertical magnetic field B. At an instant t, the wire is given a small velocity vtowards right. (a) Find the current in it at this instant. What is the direction of the current? (b) What is the force acting on the wire at this instant? (c) Show that after some time the wire ab will slide with a constant velocity. Find this velocity.

Solution
According to Fleming's left hand rule the force in the wire ab will be in the upward direction.
Moreover, a moving wire ab is equivalent to a battery of emf vBl as shown in the figure.
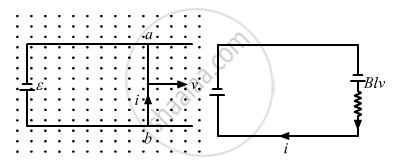
At the given instant, the net emf across the wire (e) is E − Bvl.
(a) The current through the wire is given by
\[i = \frac{E - Bvl}{r}\]
The direction of the current is from b to a.
(b) The force acting on the wire at the given instant is given by
\[F = ilB = \left( \frac{E - Bvl}{r} \right)\]towards right
(c) The velocity of the wire attains a value such that it satisfies E = Bvl.
The net force on the wire becomes zero. Thus, the wire moves with a constant velocity v.
\[\therefore v = \frac{E}{Bl}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the relation between the velocity of propagation and the magnitudes of electric and magnetic fields.
How does the path followed by the charge get affected if its velocity has a component parallel to \[\vec{B}\] .
Velocity of light in glass is 2 × 108 m/s and in air is 3 × 108 m/s. If the ray of light passes from glass to air, calculate the value of critical angle.
Suppose a charged particle moves with a velocity v near a wire carrying an electric current. So, a magnetic force acts on it. If the same particle is seen from a frame moving with velocity v in the same direction, the charge will be found to be at rest. Will the magnetic force become zero in this frame? Will the magnetic field become zero in this frame?
What is the ratio of the velocity of the wave in the two media of refractive indices μ1 and μ2?
A potential difference V is applied across a conductor of length L and diameter D. How is the drift velocity, vd, of charge carriers in the conductor affected when (i) V is halved, (ii) L is doubled and (iii) D is halved ? justify your answer in each case.
In an inertial frame of reference, the magnetic force on a moving charged particle is `vec"F"`. Its value in another inertial frame of reference will be ______.
