Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
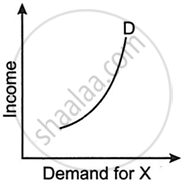
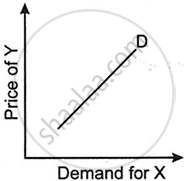
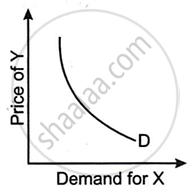
Figures (A), (B) and (C) given below represent different types of Demand curves.
 |
 |
 |
| (A) | (B) | (C) |
What kind of goods do each of these Demand curves represent? Give a reason for each of the curves.
Solution
Figure (A) shows a demand curve that slopes upward with income on the Y-axis and Demand for X on the X-axis, representing normal items whose demand increases as the consumer's income rises.
Figure (B) shows a straight upward sloping demand curve with Demand for X on the X-axis and Price of Y on the Y-axis, representing substitute goods. As the price of the substitute goods increases, so does the demand for the other goods.
Figure (C) shows demand for X on the X-axis and price for Y on the Y-axis, with the demand curve representing demand for complementary items, where an increase in the price of complementary goods causes a decrease in demand for other goods and vice versa.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State and explain the ‘law of demand’ with its exceptions.
Prices of other goods and demand for the given good.
Good Y is a substitute of good X. The price of Y falls. Explain the chain of effects of this change in the market of X.
Write explanatory notes or answer the following.
Aggregate demand
Do you agree with the following statement? Give reason
There are no exceptions to the law of demand.
State with reasons whether you ‘agree’ or ‘disagree’ with the following statement.
Demand curve slopes downward from left to right.
Statements related to decrease in demand
- It is a type of change in demand
- It takes place due to unfavourable changes in other factors like tastes, income etc.
- Price remains constant
- Demand curve shifts to the right hand side of the original demand curve
Assertion (A): Under exceptional cases, demand curve has a positive slope.
Reasoning (R): In exceptional cases, consumer buys more when the price of a commodity rises and buys less when the price of commodity falls.
The shape of supply curve is ______
The demand curve for foreign exchange is ______
Identify the correctly matched items from Column I to that of Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Demand Curve of Perfect Competition | (a) V-shaped Curve |
| (2) Demand Curve of Monopoly | (b) U-shaped Curve |
| (3) Demand Curve of Monopolistic Competition | (c) Upward rising |
| (4) Demand Curve of Oligopoly | (d) In-determinant |
Assertion (A): The demand curve is downward sloping.
Reason (R): The income effect means with a fall in the price of a good, the consumer's real income or purchasing power rises and he demands more units of the good.
Explain why the demand curve slopes downwards.
Study the following diagram and answer the questions:
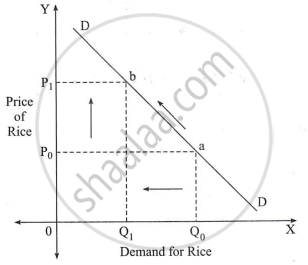
Questions:
- In which direction does the demand curve slope?
- What is the reason for the fall in demand of rice from Q0 to Q1?
