Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Give a scientific reason:
Carbon monoxide is highly dangerous when inhaled.
Give a suitable biological reason for the following statement:
Carbon monoxide is dangerous when inhaled.
Carbon monoxide is dangerous when inhaled in excess. Comment on the statement.
Solution 1
Carbon monoxide, when inhaled and absorbed into the blood, binds with haemoglobin and forms an irreversible complex called carboxyhaemoglobin. The formation of this complex reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Hence, carbon monoxide is highly dangerous when inhaled.
Solution 2
Carbon monoxide is damaging to the body because it replaces oxygen in the blood when we breathe in air. Keeping things under control. This lack of oxygen has an impact on crucial organs such as the heart, brain, and other important body parts. Inhaling significant amounts of CO can swiftly cause unconsciousness and suffocation without warning. When carbon monoxide is inhaled, it binds to haemoglobin and causes a persistent oxygen deficit in the body. Clearing CO-contaminated haemoglobin (carboxyhaemoglobin) necessitates prolonged exposure to fresh air or oxygen.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Mitochondria are regarded as semiautonomous organelles, due to the presence of ______.
One of the following does not have a nucleus. This one is:
The diagram below shows part of the capillary bed in an organ of the human body. Some of the blood arriving at the capillaries at points labeled A, moves out into the spaces between the tissue cells. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
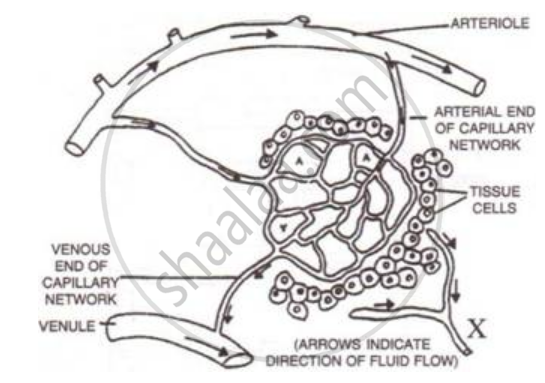
Name any one important component of the blood which remains inside the capillaries and fails to move out into the spaces.
Differentiate between the following pair of terms: RBC and WBC
The red-coloured pigment present in RBCs is called ______.
Which one of the following shows the correct composition of blood?
Given below is the diagram of a human blood smear. Label the parts numbered 1, 2 and 3.

Name the following:
The respiratory pigment contained in RBCs.
Name the following:
Any two organelles absent in mature RBCs.
Give reasons/explain:
A mature mammalian Erythrocyte lacks nucleus, mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
