Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Give an account of the Blue-White Method of selection of recombinants
Solution
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology is the technique of manipulating the genome of a cell or
the organism so as to change the phenotype desirably
Following are the basic steps involved in the process:
1) Isolating genomic DNA of a ‘donor’. The cell or organism from which the required gene is taken is called ‘donor’
2) Fragmenting this DNA using “molecular scissors’ (Enzymes): Different enzymes used are; restriction endonucleases, DNA ligase, reverse transcriptase, DNA polymerase, alkaline phosphatases etc. The restriction endonucleases are used to cut DNA at specific points. They are called biological / molecular / chemical scissors / knives / scalpels.
3) Screening the fragments for a ‘desired gene’
4) Inserting the fragments with the desired gene into a ‘cloning vector’ - Vectors are the DNA molecules used to transfer genetic material into another cell. (a plasmid, cosmid or phage DNA), so as to develop a recombinant DNA or chimeric DNA.
5) Introducing the recombinant vector into a competent host cell.
6) Culturing these cells to obtain multiple copies or clones of the desired fragment of DNA.
7) Using these copies to “Transform” suitable host cells so as to express the desired gene.

8) Selection of transformants by the blue-white method of selection of recombinants.
It is a screening technique that allows for rapid and convenient detection of recombinant bacteria in vector – based molecular cloning experiments. Recombinant DNA is inserted into a competent host cell viable for transformation, which is then grown in presence of X – gal. The cell transformed with vectors containing Recombinant DNA will produce white colonies, cells transformed with non – recombinant plasmids (i.e. only the vector) grow into blue colonies. This method of screening is usually performed using a suitable bacterial strain, but other organisms such as yeast may also be used.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the role of DNA ligase in biotechnology.
Explain the properties of a good or ideal cloning vector for rDNA technology.
From the following which one is NOT a feature of the plasmids?
From the following list of cloning vectors used in rDNA technology identify the vectors that are the most commonly used.
Plasmids, bacteriophages (Ml3, lambda virus), cosmid, phagemid, BAC (bacterial artificial chromosome), YAC (yeast artificial chromosome), transposons, baculoviruses, and mammalian artificial chromosomes (MACs)
Which of the following is NOT involved in genetic engineering technique?
i. Combining genes from two organisms
ii. Gene cloning
iii. Transfer of lipid molecules
iv. Transfer of genes to new organisms
v. Repairing or replacing the defective genes by healthy genes
vi. Artificial synthesis of new gene
Annealing step of PCR operates at ______ °C.
Which of the following is the correct recognition sequence of restriction enzyme Eco RI?
Name two restriction enzymes used in PCR.
The given figure is the diagrammatic representation of the E. coli vector pBR322. Which one of the given options correctly indentites its certain component(s)?
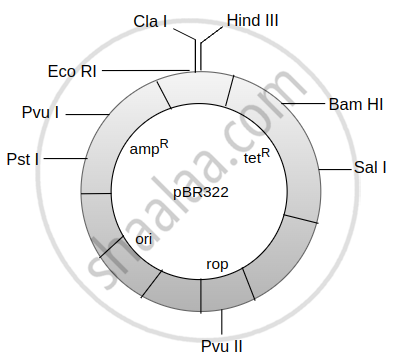
Which of these are most widely used in genetic engineering?
