Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Give any two effects of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Solution
- In the presence of carbon monoxide, haemoglobin readily combines to form a stable compound called carboxyhaemoglobin.
- The formation of carboxyhaemoglobin prevents the binding of oxygen with haemoglobin and less haemoglobin is available for oxygen transport depriving the cells of oxygen.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The size of the chest cavity increases during inhalation.
Make the correct pairs.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| (P) IC | i. maximum volume of air breathe in after forced. |
| (Q) EC | ii. Volume of air present after expiration in lungs. |
| (R) VC | iii. Volume of air inhaled after expiration. |
| (S) FRC | iv. Volume of air present after expiration in lungs. |
______ is formed when carbon monoxide combines with haemoglobin.
Which of the following part becomes flat during inspiration?
Which of the following is formed in RBCs when CO2 combines with H2O in presence of carbonic anhydrase?
The impulse for voluntary muscles for forced breathing starts in ____________.
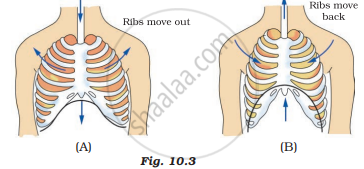
Observe the figures given in Figures 10.3 (A) and (B) and answer the following.
Which of the figures A or B indicates the process of inhalation and which is the process of exhalation?
In alveolar air, the partial pressure of CO2 is ______.
Listed below are four respiratory capacities (1 - 4) and four jumbled respiratory volumes of a normal human adult
| Respiratory Capacities | Respiratory Volumes |
| 1. Residual volume | 2500 mL |
| 2. Vital capacity | 5500 mL |
| 3. Inspiratory sore volume | 1200 mL |
| 4. Total Lung capacity | 4500 mL |
Which one of the following is the correct matching of two capacities and volumes?
What is oxygen dissociation curve?
