Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Give the general characteristics of organic compounds.
Solution
All organic compounds have the following characteristic properties.
- They are covalent compounds of carbon and generally insoluble in water and readily soluble in organic solvent such as benzene, toluene, ether, chloroform etc…
- Many of the organic compounds are inflammable (except CCl4). They possess low boiling and melting points due to their covalent nature.
- Organic compounds are characterized by functional groups. A functional group is an atom or a specific combination of bonded atoms that react in a characteristic way, irrespective of the organic molecule in which it is present. In almost all cases, the reaction of an organic compound takes place at the functional group. They exhibit isomerism which is a unique phenomenon.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a formula for the first five members of the homologous series beginning with the given compound.
H–COOH
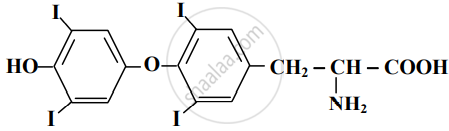
Find out all the functional groups present in the following polyfunctional compound.
Thyroxine, the principal thyroid hormone.
Write the molecular formula and possible structural formula of the first four members of homologous series of carboxylic acids.
An organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is soluble in dil. H2SO4 and does not react with sodium metal or KMnO4. When it is heated with HI in excess, a single alkyl halide is obtained. The original compound can be ____________.
Which of the following is a hetero-aromatic benzenoid compound?
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT for the organic compounds which belong to homologous series?
The correct decreasing order of priority for the functional groups of organic compounds in the IUPAC system of nomenclature is ______.
Identify primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary carbon in the following compound.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..................}\\
|\phantom{....................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH - CH2 - CH2 - CH3}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{................}\\
\ce{CH3} \ce{CH3}\phantom{..............}
\end{array}\]
Identify the α - carbons in the following species and give the total number of
\[\ce{CH3 -CH2 -\overset{⊕}{C}H -CH2 -CH3}\]
Identify primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary carbon in the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\\
|\phantom{....................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH - CH2 - CH2 - CH3}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\ce{CH3}\phantom{..............}\\
\end{array}\]
