Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How are the lungs designed in human beings to maximize the area for exchange of gases?
Solution 1
Lungs contain millions of alveoli which provide a surface for the exchange of gases. An extensive network of blood vessels is present in the wall of the alveoli. By lifting our ribs and flatten the diaphragm, the chest cavity becomes spacious. Air is sucked into the lungs and alveoli. The oxygen from the breath, diffuses into the blood and CO2 from the blood brought from the body, diffuses out into the air.
Solution 2
- Human lungs contain a highly branched system of respiratory tubes. A primary bronchus splits into secondary bronchi, which then form tertiary bronchi. Each tertiary bronchus further divides into bronchioles that end in alveoli. Alveoli are small, rounded, thin-walled pouches with a network of capillaries.
- Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli, which is why each alveolus is considered a miniature lung. The alveoli offer a large surface area for gas exchange. Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the pulmonary capillaries, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the capillaries into the alveoli. The total surface area of the alveoli in human lungs is estimated to be about 100 m².
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Carbon dioxide enters into the leaves through tiny pores present on the surface of the leaf called _________.
(a) chlorophyll
(b) chloroplast
(c) stomata
(d) epidermis
How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
The mountaineers carry oxygen with them because ______.
What would happen if all the green plants disappear from the earth?
Name one substance which is produced in anaerobic respiration by an organism but not in aerobic respiration.
Name two animals which breathe through gills.
State whether the following statement is true or false:
during respiration, the plants take CO2 and release O2.
Explain how, it would benefit deep sea divers if humans also had gills.
Which of the following is correct for the process of anaerobic respiration?
| Carbon dioxide always produced | A lot of energy released | |
| (a) | No | Yes |
| (b) | No | No |
| (c) | Yes | No |
| (d) | Yes | Yes |
Which of the following is the correct sequence of air passage during inhalation?
(a) nostrils → larynx → pharynx → trachea → lungs
(b) nasal passage → trachea → pharynx → larynx → alveoli
(c) larynx → nostrils → pharynx → lungs
(d) nostrils → pharynx → larynx → trachea → alevoli
Which of the following is known as the energy currency of the cells in biology?
One of the following animals does not use tracheae as the respiratory organs. This animal is:
Which of the following is most likely to have a much higher breathing rate?
In cockroaches, air enters the body through:
During the respiration of an organism A, 1 molecule of glucose produces 2 ATP molecules whereas in the respiration of another organism B, 1 molecule of glucose produces 38 ATP molecules.
(a) Which organism is undergoing aerobic respiration?
(b) Which organism is undergoing anaerobic respiration?
(c) Which type of organism, A or B, can convert glucose into alcohol?
(d) Name one organism which behaves like A.
(e) Name two organisms which behave like B.
What is the name of tissues which transport:
water and minerals in a plant?
What happens to the glucose which enters the nephron tubule alongwith the filtrate?
An animal in which the oxygenation of blood does not take place in the lungs is:
There is a pair of bean-shaped organs P in the human body towards the back, just above the waist. A waste product Q formed by the decomposition of unused proteins in the liver is brought into organ P through blood by an artery R. The numerous tiny filters S present in organ P clean the dirty blood by removing the waste product Q. The clean blood goes into circulation through a vein T. The waste substance Q, other waste salts, and excess water form a yellowish liquid U which goes from organ P into a bag-like structure V through two tubes W. This liquid is then thrown out of the body through a tube X.
(a) What is (i) organ P, and (ii) waste substance Q?
(b) Name (i) artery R, and (ii) vein T.
(c) What are tiny filters S known as?
(d) Name (i) liquid U (ii) structure V (iii) tubes W, and (iv) tube X.
Out of xylem and phloem, which one carries materials only upwards?
Answer the following in detail.
Explain the process of Cellular Respiration.
What is the normal percentage composition of gases in inspired and expired air respectively?
Match the items in Column I with the ones most appropriate in Column II. Rewrite the matching pairs.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(a) Alveoli |
(i) where aerobic respiration takes place |
|
(b) Bronchioles |
(ii) lined with hair |
|
(c) Nasal Chamber |
(iii) diffusion of gases |
|
(d) Bronchi |
(iv) small air tubes |
|
(v) an inverted Y shaped tube |
|
|
(vi) a common passage for food and air |
State one function of the following:
Diaphragm
List the organs of Human respiratory system.
Answer the following question.
A gas is released during photosynthesis. Name the gas and also state the way by which the gas is evolved.
Define respiration.
Identify the CORRECT sequence of events for the transport of respiratory gases.
Which of the following indicates the shift of oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve due to change in ppC02 in blood?
Lack of oxygen in muscles often leads to cramps among cricketers. This results due to:
Glycolysis process occurs in which part of the cell?
Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true about respiration?
- During inhalation, ribs move inward and the diaphragm is raised
- In the alveoli, exchange of gases takes place i.e., oxygen from alveolar air diffuses into blood and carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveolar air
- Haemoglobin has a greater affinity for carbon dioxide than oxygen
- Alveoli increase surface area for the exchange of gases
During respiration exchange of gases take place in
Breathing is a process that
- provides O2 to the body.
- breaks down food to release energy.
- helps the body to get rid of CO2.
- produces water in the cells.
Which of the following gives the correct combination of functions of breathing?
Observe Figure 10.2 carefully and answer the following questions.
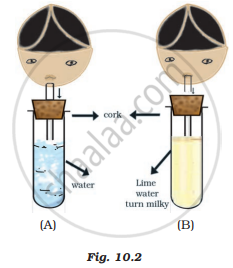
- Which process is being tested in the activity?
- What is the result of the activity? Give reasons.
